Vg1RBP phosphorylation by Erk2 MAP kinase correlates with the cortical release of Vg1 mRNA during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes
- PMID: 19376927
- PMCID: PMC2685525
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1195709
Vg1RBP phosphorylation by Erk2 MAP kinase correlates with the cortical release of Vg1 mRNA during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes
Abstract
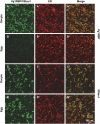
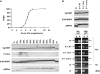
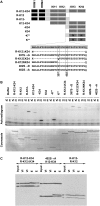
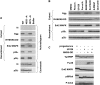
Xenopus Vg1RBP is a member of the highly conserved IMP family of four KH-domain RNA binding proteins, with roles in RNA localization, translational control, RNA stability, and cell motility. Vg1RBP has been implicated in localizing Vg1 mRNAs to the vegetal cortex during oogenesis, in a process mediated by microtubules and microfilaments, and in migration of neural crest cells in embryos. Using c-mos morpholino, kinase inhibitors, and constitutely active recombinant kinases we show that Vg1RBP undergoes regulated phosphorylation by Erk2 MAPK during meiotic maturation, on a single residue, S402, located between the KH2 and KH3 domains. Phosphorylation temporally correlates with the release of Vg1 mRNA from its tight cortical association, assayed in lysates in physiological salt buffers, but does not affect RNA binding, nor self-association of Vg1RBP. U0126, a MAP kinase inhibitor, prevents Vg1RBP cortical release and Vg1 mRNA solubilization in meiotically maturing eggs, while injection of MKK6-DD, a constitutively activated MAP kinase kinase, promotes the release of both Vg1RBP and Vg1 mRNA from insoluble cortical structures. We propose that Erk2 MAP kinase phosphorylation of Vg1RBP regulates the protein:protein-mediated association of Vg1 mRNP with the cytoskeleton and/or ER. Since the MAP kinase site in Vg1RBP is conserved in several IMP homologs, this modification also has important implications for the regulation of IMP proteins in somatic cells.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso G., Ambrosino C., Jones M., Nebreda A.R. Differential activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms depending on signal strength. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:40641–40648. - PubMed
-
- Becker B.E., Gard D.L. Visualization of the cytoskeleton in Xenopus oocytes and eggs by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006;322:69–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
