Myosin-dependent targeting of transmembrane proteins to neuronal dendrites
- PMID: 19377470
- PMCID: PMC2937175
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2318
Myosin-dependent targeting of transmembrane proteins to neuronal dendrites
Abstract
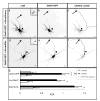
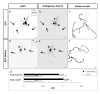
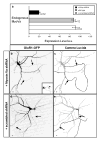
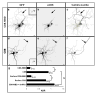
The distinct electrical properties of axonal and dendritic membranes are largely a result of specific transport of vesicle-bound membrane proteins to each compartment. How this specificity arises is unclear because kinesin motors that transport vesicles cannot autonomously distinguish dendritically projecting microtubules from those projecting axonally. We hypothesized that interaction with a second motor might enable vesicles containing dendritic proteins to preferentially associate with dendritically projecting microtubules and avoid those that project to the axon. Here we show that in rat cortical neurons, localization of several distinct transmembrane proteins to dendrites is dependent on specific myosin motors and an intact actin network. Moreover, fusion with a myosin-binding domain from Melanophilin targeted Channelrhodopsin-2 specifically to the somatodendritic compartment of neurons in mice in vivo. Together, our results suggest that dendritic transmembrane proteins direct the vesicles in which they are transported to avoid the axonal compartment through interaction with myosin motors.
Figures

References
-
- Mostov K, Su T, ter Beest M. Polarized epithelial membrane traffic: conservation and plasticity. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Folsch H, Ohno H, Bonifacino JS, Mellman I. A novel clathrin adaptor complex mediates basolateral targeting in polarized epithelial cells. Cell. 1999;99:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Burack MA, Silverman MA, Banker G. The role of selective transport in neuronal protein sorting. Neuron. 2000;26:465–472. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda S, et al. Accumulation of AMPA receptors in autophagosomes in neuronal axons lacking adaptor protein AP-4. Neuron. 2008;57:730–745. - PubMed
-
- Setou M, et al. Glutamate-receptor-interacting protein GRIP1 directly steers kinesin to dendrites. Nature. 2002;417:83–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

