Efficacy and safety of tadalafil taken as needed for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in Asian men: results of an integrated analysis
- PMID: 19377488
- PMCID: PMC3735316
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2009.11
Efficacy and safety of tadalafil taken as needed for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in Asian men: results of an integrated analysis
Abstract
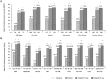
We evaluated the efficacy and safety of as-needed tadalafil in a diverse clinical population (with varying patient demographics, disease severity, and comorbid medical conditions) of Asian men with erectile dysfunction (ED). An integrated analysis of five double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (N = 1 046) was performed. Patients were randomly assigned to receive 10 mg tadalafil (N = 185), 20 mg tadalafil (N = 510), or placebo (N = 351). Efficacy assessments included the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF), Sexual Encounter Profile (SEP) diary and Global Assessment Question (GAQ). Patients receiving 10 mg or 20 mg tadalafil showed significant improvement from baseline-to-end point on the Erectile Function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-EF) domain score in all clinical sub-populations analyzed, compared with patients receiving placebo (P < 0.001). The 10-mg and 20-mg tadalafil groups showed a mean success rate of 64.1% and 70.5% for sexual intercourse attempts (SEP3, successful intercourse), respectively, compared with 33.4% in the placebo group (P < 0.001), and 85.5% and 85.4% reported improved erections at end point GAQ, respectively, versus 43.5% in the placebo group (P < 0.001). Tadalafil was well tolerated across all groups studied. Headache and back pain were the most frequently reported adverse events. Overall, tadalafil was effective and well tolerated across a diverse clinical spectrum of Asian men with ED.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of tadalafil in a Western European population of men with erectile dysfunction.BJU Int. 2004 Oct;94(6):871-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05049.x. BJU Int. 2004. PMID: 15476525 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of on-demand tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in South-East Asian men.Int J Urol. 2006 Jun;13(6):721-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2006.01393.x. Int J Urol. 2006. PMID: 16834650 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of tadalafil in clinical populations.J Sex Med. 2005 Jul;2(4):517-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2005.00068.x. J Sex Med. 2005. PMID: 16422847
-
Efficacy and safety of tadalafil once daily: considerations for the practical application of a daily dosing option.Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 Dec;24(12):3383-92. doi: 10.1185/03007990802498440. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008. PMID: 19032120 Review.
-
Tadalafil.Drugs. 2003;63(20):2203-12; discussion 2213-4. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363200-00004. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 14498756 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and medical management of erectile dysfunction in Asia.Asian J Androl. 2011 Jul;13(4):543-9. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.131. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Asian J Androl. 2011. PMID: 21460862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A real-world pilot study assessing treatment satisfaction with avanafil in patients with erectile dysfunction.Sex Med. 2024 Feb 7;12(1):qfae001. doi: 10.1093/sexmed/qfae001. eCollection 2024 Feb. Sex Med. 2024. PMID: 38327712 Free PMC article.
-
Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels and Response to 5 mg Tadalafil Once Daily in Patients With Erectile Dysfunction and Diabetes.Korean J Urol. 2013 Dec;54(12):858-64. doi: 10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.858. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Korean J Urol. 2013. PMID: 24363868 Free PMC article.
-
Routine cardiac assessment is not necessary for all patients with erectile dysfunction.Can Urol Assoc J. 2011 Oct;5(5):349-51. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.11218. Can Urol Assoc J. 2011. PMID: 22031617 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–6. - PubMed
-
- Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Billups KL. Erectile dysfunction as an early sign of cardiovascular disease. Int J Impot Res. 2005;17 Suppl 1:S19–24. - PubMed
-
- Maas R, Schwedhelm E, Albsmeier J, Boger RH. The pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction related to endothelial dysfunction and mediators of vascular function. Vasc Med. 2002;7:213–25. - PubMed
-
- Greenstein A, Chen J, Miller H, Matzkin H, Villa Y, et al. Does severity of ischemic coronary disease correlate with erectile function. Int J Impot Res. 1997;9:123–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

