Image quality optimization and evaluation of linearly mixed images in dual-source, dual-energy CT
- PMID: 19378762
- PMCID: PMC2672422
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3077921
Image quality optimization and evaluation of linearly mixed images in dual-source, dual-energy CT
Abstract
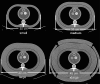
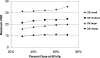
In dual-source dual-energy CT, the images reconstructed from the low- and high-energy scans (typically at 80 and 140 kV, respectively) can be mixed together to provide a single set of nonmaterial-specific images for the purpose of routine diagnostic interpretation. Different from the material-specific information that may be obtained from the dual-energy scan data, the mixed images are created with the purpose of providing the interpreting physician a single set of images that have an appearance similar to that in single-energy images acquired at the same total radiation dose. In this work, the authors used a phantom study to evaluate the image quality of linearly mixed images in comparison to single-energy CT images, assuming the same total radiation dose and taking into account the effect of patient size and the dose partitioning between the low-and high-energy scans. The authors first developed a method to optimize the quality of the linearly mixed images such that the single-energy image quality was compared to the best-case image quality of the dual-energy mixed images. Compared to 80 kV single-energy images for the same radiation dose, the iodine CNR in dual-energy mixed images was worse for smaller phantom sizes. However, similar noise and similar or improved iodine CNR relative to 120 kV images could be achieved for dual-energy mixed images using the same total radiation dose over a wide range of patient sizes (up to 45 cm lateral thorax dimension). Thus, for adult CT practices, which primarily use 120 kV scanning, the use of dual-energy CT for the purpose of material-specific imaging can also produce a set of non-material-specific images for routine diagnostic interpretation that are of similar or improved quality relative to single-energy 120 kV scans.
Figures



References
-
- Flohr T. G., McCollough C. H., Bruder H., Petersilka M., Gruber K., Suss C., Grasruck M., Stierstorfer K., Krauss B., Raupach R., Primak A. N., Kuttner A., Achenbach S., Becker C., Kopp A., and Ohnesorge B. M., “First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system,” Eur. Radiol. 16, 256–268 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Johnson T. R., Krauss B., Sedlmair M., Grasruck M., Bruder H., Morhard D., Fink C., Weckbach S., Lenhard M., Schmidt B., Flohr T., Reiser M. F., and Becker C. R., “Material differentiation by dual energy CT: Initial experience,” Eur. Radiol. 17, 1510–1517 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Scheffel H., Stolzmann P., Frauenfelder T., Schertler T., Desbiolles L., Leschka S., Marincek B., and Alkadhi H., “Dual-energy contrast-enhanced computed tomography for the detection of urinary stone disease,” Invest. Radiol. 42, 823–829 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

