Membrane-dependent interaction of factor Xa and prothrombin with factor Va in the prothrombinase complex
- PMID: 19378973
- PMCID: PMC2693874
- DOI: 10.1021/bi900240g
Membrane-dependent interaction of factor Xa and prothrombin with factor Va in the prothrombinase complex
Abstract
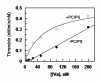
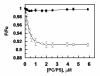
Because all three protein components of prothrombinase, factors (f) Xa and Va and prothrombin, bind to negatively charged membrane phospholipids, the exact role of the membrane in the prothrombinase reaction has not been fully understood. In this study, we prepared deletion derivatives of fXa and prothrombin in which both the Gla and first EGF-like domains of the protease (E2-fXa) as well as the Gla and both kringle domains of the substrate (prethrombin-2) had been deleted. The fVa-mediated catalytic activity of E2-fXa toward prethrombin-2 was analyzed in both the absence and presence of phospholipids composed of 80% phosphatidylcholine (PC) and 20% phosphatidylserine (PS). PCPS markedly accelerated the initial rate of prethrombin-2 activation by E2-fXa, with the cofactor exhibiting saturation only in the presence of phospholipids (apparent K(d) of approximately 60 nM). Competitive kinetic studies in the presence of the two exosite-1-specific ligands Tyr(63)-sulfated hirudin(54-65) and TM456 suggested that while both peptides are highly effective inhibitors of the fVa-mediated activation of prethrombin-2 by E2-fXa in the absence of PCPS, they are ineffective competitors in the presence of phospholipids. Since neither E2-fXa nor prethrombin-2 can interact with membranes, these results suggest that interaction of fVa with PCPS improves the affinity of the activation complex for proexosite-1 of the substrate. Direct binding studies employing OG(488)-EGR-labeled fXa and E2-fXa revealed that the interaction of the Gla domain of fXa with PCPS also induces conformational changes in the protease to facilitate its high-affinity interaction with fVa.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bothrojaracin, a proexosite I ligand, inhibits factor Va-accelerated prothrombin activation.Thromb Haemost. 2002 Feb;87(2):288-93. Thromb Haemost. 2002. PMID: 11858489
-
Contribution of the prothrombin fragment 2 domain to the function of factor Va in the prothrombinase complex.Biochemistry. 1997 Mar 18;36(11):3319-30. doi: 10.1021/bi9623993. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9116010
-
The interaction of fragment 1 of prothrombin with the membrane surface is a prerequisite for optimum expression of factor Va cofactor activity within prothrombinase.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Mar;99(3):511-22. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18327399
-
Factor Va-factor Xa interactions: molecular sites involved in enzyme:cofactor assembly.Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2002;237:5-11. doi: 10.1080/003655102762377439. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12570161 Review.
-
Blood coagulation factor Va's key interactive residues and regions for prothrombinase assembly and prothrombin binding.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Aug;17(8):1229-1239. doi: 10.1111/jth.14487. Epub 2019 Jun 17. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31102425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mice with reduced protease-activated receptor 4 reactivity show decreased venous thrombosis and platelet procoagulant activity.J Thromb Haemost. 2025 Apr;23(4):1278-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.12.031. Epub 2025 Jan 9. J Thromb Haemost. 2025. PMID: 39798922 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylserine's role in Ebola's inflammatory cytokine storm and hemorrhagic consumptive coagulopathy and the therapeutic potential of annexin V.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Feb;135:109462. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109462. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 31731057 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the NH2-terminal EGF-domain of factor IXa to the specificity of intrinsic tenase.Thromb Haemost. 2012 Dec;108(6):1154-64. doi: 10.1160/TH12-06-0436. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 23014580 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of prothrombin with a phospholipid surface: evidence for a membrane-induced conformational change.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Feb;348(1-2):109-15. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0644-x. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21080035
-
Procoagulant adaptation of a blood coagulation prothrombinase-like enzyme complex in australian elapid venom.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jun;2(6):1554-67. doi: 10.3390/toxins2061554. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 21127733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mann KG, Jenny RJ, Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1988;57:915–956. - PubMed
-
- Rosing J, Tans G, Govers-Riemslag JWP, Zwaal RFA, Hemker HC. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:274–283. - PubMed
-
- Furie B, Furie BC. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988;53:505–518. - PubMed
-
- Davie EW, Fujikawa K, Kisiel W. The coagulation cascade: Initiation, maintenance and regulation. Biochemistry. 1991;30:10363–10370. - PubMed
-
- Jackson CM, Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

