Activating mutations of N-WASP alter Shigella pathogenesis
- PMID: 19379711
- PMCID: PMC2697925
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.050
Activating mutations of N-WASP alter Shigella pathogenesis
Abstract
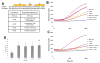
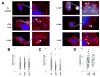
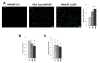
The pathogenesis of Shigella requires binding to the host protein N-WASP. To examine the roles of structural conformation and phospho-regulation of N-WASP during Shigella pathogenesis, mutant N-WASP constructs predicted to result in a constitutively open conformation (L229P and L232P) or either a phospho-mimicking (Y253E) or phospho-disruptive (Y253F) structure were constructed. Pyrene actin assays demonstrated that the N-WASP L229P and L232P constructs are constitutively active. Despite the increase in actin polymerization seen in vitro, cell lines expressing N-WASP L229P and L232P supported shorter actin tails when infected with Shigella. Shigella actin tails were unchanged in cells expressing N-WASP phospho-regulation mutant proteins. Shigella invasion, intracellular, and intercellular motility were not altered in cells expressing N-WASP L229P or L232P. However, plaque numbers were increased in cells expressing N-WASP L229P and L232P. These data demonstrate that N-WASP structural conformation is an important regulator of Shigella pathogenesis in distinct segments of its lifecycle.
Figures
References
-
- Gouin E, Welch MD, Cossart P. Actin-based motility of intracellular pathogens. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:35–45. - PubMed
-
- Takenawa T, Suetsugu S. The WASP-WAVE protein network: connecting the membrane to the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Miki H, Takenawa T. Direct binding of the verprolin-homology domain in N-WASP to actin is essential for cytoskeletal reorganization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;243:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Kim AS, Kakalis LT, Abdul-Manan N, Liu GA, Rosen MK. Autoinhibition and activation mechanisms of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein. Nature. 2000;404:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Suetsugu S, Hattori M, Miki H, Tezuka T, Yamamoto T, Mikoshiba K, Takenawa T. Sustained activation of N-WASP through phosphorylation is essential for neurite extension. Dev Cell. 2002;3:645–658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

