Inhibition of the human neutrophil NADPH oxidase by Coxiella burnetii
- PMID: 19379824
- PMCID: PMC2704257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.04.005
Inhibition of the human neutrophil NADPH oxidase by Coxiella burnetii
Abstract
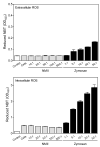
Coxiella burnetii is an obligate intracellular Gram-negative pathogen. A notable feature of C. burnetii is its ability to replicate within acidic phagolysosomes; however, the mechanisms utilized in evading host defenses are not well defined. Here, we investigated human neutrophil phagocytosis of C. burnetii (Nine Mile, phase II; NMII) and the effect of phagocytosed organisms on neutrophil reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. We found that opsonization with immune serum substantially enhanced phagocytosis of NMII. Human neutrophils phagocytosing opsonized NMII generated very little ROS compared to cells phagocytosing opsonized Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, or zymosan. However, phagocytosis of NMII did not affect the subsequent ROS response to a soluble agonist, indicating inhibition was localized to the phagolysosome and was not a global effect. Indeed, analysis of NADPH oxidase assembly in neutrophils after phagocytosis showed that translocation of cytosolic NADPH oxidase proteins, p47(phox) and p67(phox), to the membrane was absent in cells phagocytosing NMII, as compared to cells phagocytosing S. aureus or activated by phorbol myristate acetate. Thus, phagocytosed NMII is able to disrupt assembly of the human neutrophil NADPH oxidase, which represents a novel virulence mechanism for this organism and appears to be a common mechanism of virulence for many intracellular pathogens.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coxiella burnetii interaction with neutrophils and macrophages in vitro and in SCID mice following aerosol infection.Infect Immun. 2013 Dec;81(12):4604-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00973-13. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24082077 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii Inhibits Neutrophil Apoptosis by Exploiting Survival Pathways and Antiapoptotic Protein Mcl-1.Infect Immun. 2018 Mar 22;86(4):e00504-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00504-17. Print 2018 Apr. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29311244 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii acid phosphatase inhibits the release of reactive oxygen intermediates in polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Infect Immun. 2011 Jan;79(1):414-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01011-10. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21078859 Free PMC article.
-
Study of NADPH oxidase-activated sites in human neutrophils.J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2002;51(2):87-91. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/51.2.87. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2002. PMID: 12005167 Review.
-
[Cooperation of membrane proteins and cytosolic proteins in metabolic regulation--involvement of binding of hexokinase to mitochondria in regulation of glucose metabolism and association and complex formation between membrane proteins and cytosolic proteins in regulation of active oxygen production].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1999 Jan;119(1):16-34. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.119.1_16. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 9922708 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Modulation of RhoGTPases improves the behavioral phenotype and reverses astrocytic deficits in a mouse model of Rett syndrome.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Apr;37(5):1152-63. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.301. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22157810 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii interaction with neutrophils and macrophages in vitro and in SCID mice following aerosol infection.Infect Immun. 2013 Dec;81(12):4604-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00973-13. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24082077 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of NADPH oxidase in modulating neutrophil effector responses.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2019 Apr;34(2):27-38. doi: 10.1111/omi.12252. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30632295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legionella pneumophila subverts the antioxidant defenses of its amoeba host Acanthamoeba castellanii.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2025 Jan 7;8:100338. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100338. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2025. PMID: 39877885 Free PMC article.
-
Virulent Coxiella burnetii pathotypes productively infect primary human alveolar macrophages.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Jun;15(6):1012-25. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12096. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23279051 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

