Phase III noninferiority trial comparing irinotecan with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma previously treated with fluorouracil: N9841
- PMID: 19380443
- PMCID: PMC2698019
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.4552
Phase III noninferiority trial comparing irinotecan with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma previously treated with fluorouracil: N9841
Abstract
Purpose: The primary goal of this multicenter phase III trial was to determine whether overall survival (OS) of fluorouracil (FU) -refractory patients was noninferior when treated with second-line infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4; arm B) versus irinotecan (arm A). Cross-over to the other treatment on disease progression was mandated.
Patients and methods: Patients who experienced treatment failure with one prior FU-based therapy and had not received prior irinotecan or oxaliplatin, either for metastatic disease or within 6 months of adjuvant FU therapy, were randomly assigned to arm A (irinotecan 350 or 300 mg/m(2) every 3 weeks) or arm B (FOLFOX4).
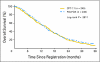
Results: A total of 491 patients were randomly assigned (arm A, n = 245; arm B, n = 246); 288 (59%) had experienced treatment failure with FU for metastatic colorectal cancer. Two hundred twenty-seven patients (46%) received protocol-mandated third-line therapy (arm A, 43%; arm B, 57%). Median survival was 13.8 months (95% CI, 12.2 to 15.0 months) for initial treatment with FOLFOX4 and 14.3 months (95% CI, 12.0 to 15.9 months) for irinotecan (P = .38; hazard ratio = 0.92; 95% CI, 0.8 to 1.1). Response rates (RR; 28% v 15.5%; P = .0009) and time to progression (TTP; 6.2 v 4.4 months; P = .0009) were significantly superior with FOLFOX4. In the nonrandom subset of patients who crossed over, RR and TTP improvements with FOLFOX4 continued into third-line treatment. Irinotecan therapy was associated with more grade 3 nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and febrile neutropenia; FOLFOX4 was associated with more neutropenia and paresthesias.
Conclusion: In patients who experienced treatment failure with front-line FU therapy, OS does not significantly differ whether second-line therapy begins with irinotecan or FOLFOX4. FOLFOX4 produces higher RR and longer TTP. Both arms had notable OS in patients who experienced treatment failure with first-line FU therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, et al. Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:905–914. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, et al. Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355:1041–1047. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs C, Marshall J, Mitchell E, et al. Updated results of BICC-C study comparing first-line irinotecan/fluoropymidine combinations with or without celecoxib in mCRC: Updated efficacy data. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(suppl):170s. abstr 4027.
-
- Rougier P, Van Cutsem E, Bajetta E, et al. Randomised trial of irinotecan versus fluorouracil by continuous infusion after fluorouracil failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1998;352:1407–1412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- U10 CA052352/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA060276/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-52352/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-60276/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical