Phase 1/2 double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, safety, and pharmacokinetic study of pagibaximab (BSYX-A110), an antistaphylococcal monoclonal antibody for the prevention of staphylococcal bloodstream infections, in very-low-birth-weight neonates
- PMID: 19380597
- PMCID: PMC2704668
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01565-08
Phase 1/2 double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, safety, and pharmacokinetic study of pagibaximab (BSYX-A110), an antistaphylococcal monoclonal antibody for the prevention of staphylococcal bloodstream infections, in very-low-birth-weight neonates
Abstract
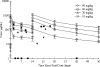
Staphylococcal sepsis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants. A human chimeric monoclonal antibody, pagibaximab, was developed against staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid. We evaluated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of pagibaximab in VLBW neonates. A phase 1/2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose escalation study was conducted in VLBW infants (700 to 1,300 g) 3 to 7 days old. Patients received two doses 14 days apart of intravenous pagibaximab (10, 30, 60, or 90 mg/kg of body weight) or placebo in a 2:1 ratio. Blood and urine samples were obtained pre- and postinfusion for analysis of safety and pharmacokinetics, and data on adverse events were gathered. Staphylococcal organisms causing sepsis were collected and evaluated. Fifty-three patients received at least one dose of pagibaximab or placebo. The average gestational age was 27.6 weeks; the average birth weight was 1,003 g. All serious adverse events were deemed unrelated or probably not drug related. Morbidity and mortality were similar across treatment groups. No evidence of immunogenicity of pagibaximab was detected. Pagibaximab pharmacokinetics was linear. The mean clearance (CL), volume of distribution, and elimination half-life of pagibaximab were independent of dose. The serum half-life was 20.5 +/- 6.8 days. Pagibaximab enhanced serum opsonophagocytic activity. All staphylococci causing sepsis were opsonizable by pagibaximab. Two infusions of pagibaximab, administered 2 weeks apart to high-risk neonates appeared safe and tolerable, and pharmacokinetics were linear. Evaluation of more frequent doses, at the highest doses tested, in neonates at high-risk of staphylococcal sepsis, is warranted.
Figures

References
-
- Angus, D. C., M. C. Birmingham, R. A. Balk, et al. 2000. E5 murine monoclonal antiendotoxin antibody in gram-negative sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 283:1723-1730. - PubMed
-
- Avery, G. B., M. A. Fletcher, and M. G. MacDonald. 1999. Neonatology: pathophysiology and management of the newborn, 5th ed., p. 1501-1534. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Azuma, J., T. Kurimoto, S. Tsuji, et al. 1991. Phase I study on human monoclonal antibody against cytomegalovirus: pharmacokinetics and immunogenicity. J. Immunother. 10:278-285. - PubMed
-
- Ballow, M., K. L. Cates, J. C. Rowe, et al. 1986. Development of the immune system in very low birth weight (less than 1500 g) premature infants: concentrations of plasma immunoglobulins and patterns of infections. Pediatr. Res. 20:899-904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

