Simplified and effective motor control based on muscle synergies to exploit musculoskeletal dynamics
- PMID: 19380738
- PMCID: PMC2678607
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901512106
Simplified and effective motor control based on muscle synergies to exploit musculoskeletal dynamics
Abstract
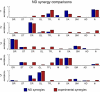
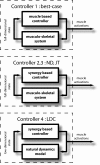
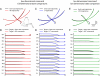
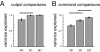
The basic hypothesis of producing a range of behaviors using a small set of motor commands has been proposed in various forms to explain motor behaviors ranging from basic reflexes to complex voluntary movements. Yet many fundamental questions regarding this long-standing hypothesis remain unanswered. Indeed, given the prominent nonlinearities and high dimensionality inherent in the control of biological limbs, the basic feasibility of a low-dimensional controller and an underlying principle for its creation has remained elusive. We propose a principle for the design of such a controller, that it endeavors to control the natural dynamics of the limb, taking into account the nature of the task being performed. Using this principle, we obtained a low-dimensional model of the hindlimb and a set of muscle synergies to command it. We demonstrate that this set of synergies was capable of producing effective control, establishing the viability of this muscle synergy hypothesis. Finally, by combining the low-dimensional model and the muscle synergies we were able to build a relatively simple controller whose overall performance was close to that of the system's full-dimensional nonlinear controller. Taken together, the results of this study establish that a low-dimensional controller is capable of simplifying control without degrading performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gottlieb GL, Song Q, Hong DA, Almeida GL, Corcos D. Coordinating movement at two joints: A principle of linear covariance. J Neurophysiol. 1996;75:1760–1764. - PubMed
-
- Bizzi E, Hogan N, Mussa-Ivaldi F, Giszter S. Does the nervous system use equilibrium-point control to guide single and multiple joint movements. Behav Brain Sci. 1992;15:603–613. - PubMed
-
- Soechting JF, Flanders M. Errors in pointing are due to approximations in sensorimotor transformations. J Neurophysiol. 1989;62:595–608. - PubMed
-
- Masino T, Knudsen EI. Horizontal and vertical components of head movement are controlled by distinct neural circuits in the barn owl. Nature. 1990;345:434–437. - PubMed
-
- Liebermann DG, Biess A, Friedman J, Gielen CC, Flash T. Intrinsic joint kinematic planning. I. Reassessing the Listing's law constraint in the control of three-dimensional arm movements. Exp Brain Res. 2006;171:139–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

