IL-7 administration drives T cell-cycle entry and expansion in HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 19380868
- PMCID: PMC2710926
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-10-186601
IL-7 administration drives T cell-cycle entry and expansion in HIV-1 infection
Abstract
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a common gamma chain receptor cytokine implicated in thymopoiesis and in peripheral expansion and survival of T lymphocytes. The safety and activity of recombinant human IL-7 (rhIL-7) administration were therefore examined in HIV-infected persons. In this prospective randomized placebo-controlled study, a single subcutaneous dose of rhIL-7 was well tolerated with biologic activity demonstrable at 3 microg/kg and a maximum tolerated dose of 30 microg/kg. Injection site reactions and transient elevations of liver function tests were the most notable side effects. Transient increases in plasma HIV-RNA levels were observed in 6 of 11 IL-7-treated patients. Recombinant hIL-7 induced CD4 and CD8 T cells to enter cell cycle; cell-cycle entry was also confirmed in antigen-specific CD8 T cells. Administration of rhIL-7 led to transient down-regulation of the IL-7 receptor alpha chain (CD127) in both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. Single-dose rhIL-7 increased the numbers of circulating CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells, predominantly of central memory phenotype. The frequency of CD4(+) T cells with a regulatory T-cell phenotype (CD25(high) CD127(low)) did not change after rhIL-7 administration. Thus, rhIL-7 has a biologic and toxicity profile suggesting a potential for therapeutic trials in HIV infection and other settings of lymphopenia. This clinical trial has been registered at http://www.clinicaltrials.gov under NCT0099671.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00099671 NCT00099671.
Figures
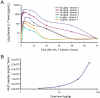
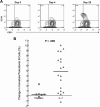
 ) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants (
) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants ( ). (B) CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell changes from baseline according to rhIL-7 dose group. ● represents placebo participants (
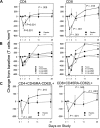
). (B) CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell changes from baseline according to rhIL-7 dose group. ● represents placebo participants ( ) and rhIL-7 participants are represented by ▲ (3 μg/kg), ■ (10 μg/kg), ♦ (30 μg/kg), and X (60 μg/kg). (C) Central memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells decreased significantly on day 1 and increased significantly on day 14 and day 28 (CD8+ T cells) after a single rhIL-7 administration. ● represents placebo participants (
) and rhIL-7 participants are represented by ▲ (3 μg/kg), ■ (10 μg/kg), ♦ (30 μg/kg), and X (60 μg/kg). (C) Central memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells decreased significantly on day 1 and increased significantly on day 14 and day 28 (CD8+ T cells) after a single rhIL-7 administration. ● represents placebo participants ( ) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants (
) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants ( ).
).
 ) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants (
) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants ( ).
).
 ) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants (
) and ▲ represents rhIL-7 participants ( ). (C) Absolute counts of Ki67+ T cells during study participation by rhIL-7 dose. ● represents placebo participants (
). (C) Absolute counts of Ki67+ T cells during study participation by rhIL-7 dose. ● represents placebo participants ( ) and rhIL-7 participants are represented by ▲ (3 μg/kg), ■ (10 μg/kg), ♦ (30 μg/kg), and X (60 μg/kg). P values represent comparisons between rhIL-7 and placebo recipients by Wilcoxon rank sum test.
) and rhIL-7 participants are represented by ▲ (3 μg/kg), ■ (10 μg/kg), ♦ (30 μg/kg), and X (60 μg/kg). P values represent comparisons between rhIL-7 and placebo recipients by Wilcoxon rank sum test.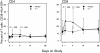
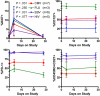
 ) and ▲ represets rhIL-7 participants (
) and ▲ represets rhIL-7 participants ( ).
).
References
-
- Fry TJ, Mackall CL. Interleukin-7: from bench to clinic. Blood. 2002;99:3892–3904. - PubMed
-
- Mazzucchelli R, Durum SK. Interleukin-7 receptor expression: intelligent design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:144–154. - PubMed
-
- Sasson SC, Zaunders JJ, Kelleher AD. The IL-7/IL-7 receptor axis: understanding its central role in T-cell homeostasis and the challenges facing its utilization as a novel therapy. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:1571–1582. - PubMed
-
- Bolotin E, Smogorzewska M, Smith S, Widmer M, Weinberg K. Enhancement of thymopoiesis after bone marrow transplant by in vivo interleukin-7. Blood. 1996;88:1887–1894. - PubMed
-
- Fry TJ, Connick E, Falloon J, et al. A potential role for interleukin-7 in T-cell homeostasis. Blood. 2001;97:2983–2990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- AI 25879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 38855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025915/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 25915/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- AI 27675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 38858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

