Cordycepin inhibits UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression by suppressing the NF-kappaB pathway in human dermal fibroblasts
- PMID: 19381070
- PMCID: PMC2739894
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2009.41.8.060
Cordycepin inhibits UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression by suppressing the NF-kappaB pathway in human dermal fibroblasts
Abstract
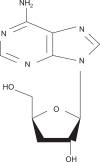
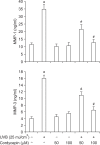
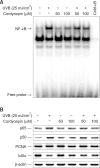
Cordycepin (3-deoxyadenosine) has been shown to exhibit many pharmacological activities, including anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and anti-infection activities. However, the anti-skin photoaging effects of cordycepin have not yet been reported. In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effects of cordycepin on matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and -3 expressions of the human dermal fibroblast cells. Western blot analysis and real-time PCR revealed cordycepin inhibited UVB-induced MMP-1 and -3 expressions in a dose-dependent manner. UVB strongly activated NF-kappaB activity, which was determined by IkappaBalpha degradation, nuclear localization of p50 and p65 subunit, and NF-kappaB binding activity. However, UVB-induced NF-kappaB activation and MMP expression were completely blocked by cordycepin pretreatment. These findings suggest that cordycepin could prevent UVB-induced MMPs expressions through inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. In conclusion, cordycepin might be used as a potential agent for the prevention and treatment of skin photoaging.
Figures

References
-
- Afaq F, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Suppression of UVB-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappa B by green tea polyphenol in SKH-1 hairless mice. Oncogene. 2003;22:9254–9264. - PubMed
-
- Bell S, Degitz K, Quirling M, Jilg N, Page S, Brand K. Involvement of NF-kappaB signalling in skin physiology and disease. Cell Signal. 2003;15:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Bond M, Baker AH, Newby AC. Nuclear factor kappaB activity is essential for matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 upregulation in rabbit dermal fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;264:561–567. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid, sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
