Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism
- PMID: 19381306
- PMCID: PMC2670432
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.07003
Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism
Abstract
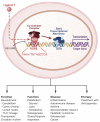
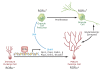
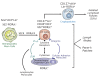
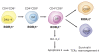
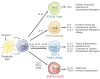
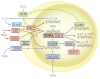
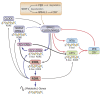
The last few years have witnessed a rapid increase in our knowledge of the retinoid-related orphan receptors RORalpha, -beta, and -gamma (NR1F1-3), their mechanism of action, physiological functions, and their potential role in several pathologies. The characterization of ROR-deficient mice and gene expression profiling in particular have provided great insights into the critical functions of RORs in the regulation of a variety of physiological processes. These studies revealed that RORalpha plays a critical role in the development of the cerebellum, that both RORalpha and RORbeta are required for the maturation of photoreceptors in the retina, and that RORgamma is essential for the development of several secondary lymphoid tissues, including lymph nodes. RORs have been further implicated in the regulation of various metabolic pathways, energy homeostasis, and thymopoiesis. Recent studies identified a critical role for RORgamma in lineage specification of uncommitted CD4+ T helper cells into Th17 cells. In addition, RORs regulate the expression of several components of the circadian clock and may play a role in integrating the circadian clock and the rhythmic pattern of expression of downstream (metabolic) genes. Study of ROR target genes has provided insights into the mechanisms by which RORs control these processes. Moreover, several reports have presented evidence for a potential role of RORs in several pathologies, including osteoporosis, several autoimmune diseases, asthma, cancer, and obesity, and raised the possibility that RORs may serve as potential targets for chemotherapeutic intervention. This prospect was strengthened by recent evidence showing that RORs can function as ligand-dependent transcription factors.
Figures

References
-
- Acosta-Rodriguez E. V., Napolitani G., Lanzavecchia A., Sallusto F. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor-β are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:942–9. - PubMed
-
- Akashi M., Takumi T. The orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha regulates circadian transcription of the mammalian core-clock Bmal1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:441–8. - PubMed
-
- Akimzhanov A. M., Yang X. O., Dong C. Chromatin remodeling of interleukin-17 (IL-17)-IL-17F cytokine gene locus during inflammatory helper T cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:5969–72. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama T. E., Gonzalez F. J. Regulation of P450 genes by liver-enriched transcription factors and nuclear receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1619:223–34. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht U. Invited review: regulation of mammalian circadian clock genes. J Appl Physiol. 2002;92:1348–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

