In vitro selection of glmS ribozymes
- PMID: 19381572
- PMCID: PMC5340292
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-59745-558-9_25
In vitro selection of glmS ribozymes
Abstract
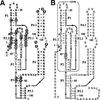
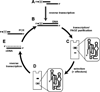
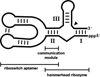
Riboswitches modulate gene expression in eubacteria and eukaryotes in response to changing concentrations of small molecule metabolites. In most examples studied to date, riboswitches achieve both metabolite sensing and gene control functions without the obligate involvement of protein factors. These findings validate the hypothesis that RNA molecules could be engineered to function as designer gene control elements that sense and respond to different ligands. We believe that reverse engineering natural riboswitches could provide an intellectual foundation for those who wish to build synthetic riboswitches. Also, natural riboswitches might serve as starting points for efforts to change ligand specificity or gene control function through mutation and selection in vitro. In this chapter, we describe how in vitro selection can be used to create variant glmS ribozymes. Additionally, we discuss how these techniques can be extended to other riboswitch classes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Examination of the structural and functional versatility of glmS ribozymes by using in vitro selection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4968-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl643. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16982640 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolite-riboswitch interactions using nucleotide analog interference mapping and suppression.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;540:193-206. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-558-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381561
-
Mechanism and distribution of glmS ribozymes.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;848:113-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-545-9_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22315066 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering ligand-responsive gene-control elements: lessons learned from natural riboswitches.Gene Ther. 2009 Oct;16(10):1189-201. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.81. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19587710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational design of allosteric ribozymes as molecular biosensors.Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Sep-Oct;32(5):1015-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 May 27. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 24877999 Review.
References
-
- Mandal M, Breaker RR. Gene regulation by riboswitches. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:451–463. - PubMed
-
- Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005;59:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Breaker RR. Riboswitches and the RNA world. In: Gesteland RF, Cech TR, Atkins JF, editors. The RNA World. Cold Spring Harbor, New York, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2006. pp. 89–107.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

