Cancer therapeutic antibodies come of age: targeting minimal residual disease
- PMID: 19383286
- PMCID: PMC5543854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2007.01.003
Cancer therapeutic antibodies come of age: targeting minimal residual disease
Abstract
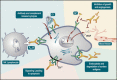
Ten years after the first clinical application of Rituximab, an anti-CD20 recombinant monoclonal antibody, immunotherapy has become common practice in oncology wards. Thanks to the great diversity of the immune system and the powerful methodology of genetic engineering, the pharmacologic potential of antibody-based therapy is far from exhaustion. The recent application of Trastuzumab, an antibody to a receptor tyrosine kinase, in adjuvant breast cancer therapy marks the beginning of a new phase in cancer treatment. Here we discuss molecular mechanisms of antibody-based therapy, the emerging ability to target minimal disease and the therapeutic potential of combining antibodies with other modalities.
Figures
References
-
- Aboud-Pirak, E. , Hurwitz, E. , Pirak, M.E. , Bellot, F. , Schlessinger, J. , Sela, M. , 1988. Efficacy of antibodies to epidermal growth factor receptor against KB carcinoma in vitro and in nude mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.. 80, 1605–1611. - PubMed
-
- Balzar, M. , Winter, M.J. , de Boer, C.J. , Litvinov, S.V. , 1999. The biology of the 17-1A antigen (Ep-CAM). J Mol. Med.. 77, 699–712. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann, C.I. , Hung, M.C. , Weinberg, R.A. , 1986. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 45, 649–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

