A single lysis solution for the analysis of tissue samples by different proteomic technologies
- PMID: 19383358
- PMCID: PMC5527781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2008.09.003
A single lysis solution for the analysis of tissue samples by different proteomic technologies
Abstract
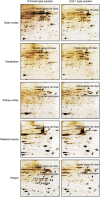
Cancer, being a major healthcare concern worldwide, is one of the main targets for the application of emerging proteomic technologies and these tools promise to revolutionize the way cancer will be diagnosed and treated in the near future. Today, as a result of the unprecedented advances that have taken place in molecular biology, cell biology and genomics there is a pressing need to accelerate the translation of basic discoveries into clinical applications. This need, compounded by mounting evidence that cellular model systems are unable to fully recapitulate all biological aspects of human dissease, is driving scientists to increasingly use clinically relevant samples for biomarker and target discovery. Tissues are heterogeneous and as a result optimization of sample preparation is critical for generating accurate, representative, and highly reproducible quantitative data. Although a large number of protocols for preparation of tissue lysates has been published, so far no single recipe is able to provide a "one-size fits all" solubilization procedure that can be used to analyse the same lysate using different proteomics technologies. Here we present evidence showing that cell lysis buffer 1 (CLB1), a lysis solution commercialized by Zeptosens [a division of Bayer (Schweiz) AG], provides excellent sample solubilization and very high 2D PAGE protein resolution both when using carrier ampholytes and immobilized pH gradient strips. Moreover, this buffer can also be used for array-based proteomics (reverse-phase lysate arrays or direct antibody arrays), allowing the direct comparison of qualitative and quantitative data yielded by these technologies when applied to the same samples. The usefulness of the CLB1 solution for gel-based proteomics was further established by 2D PAGE analysis of a number of technically demanding specimens such as breast carcinoma core needle biopsies and problematic tissues such as brain cortex, cerebellum, skeletal muscle, kidney cortex and tongue. This solution when combined with a specific sample preparation technique - cryostat sectioning of frozen specimens - simplifies tissue sample preparation and solves most of the difficulties associated with the integration of data generated by different proteomic technologies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Proteomics: technologies for protein analysis.Curr Drug Metab. 2008 Mar;9(3):213-20. doi: 10.2174/138920008783884740. Curr Drug Metab. 2008. PMID: 18336224 Review.
-
Proteomics in cancer.Adv Clin Chem. 2007;44:103-42. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(07)44004-5. Adv Clin Chem. 2007. PMID: 17682341 Review.
-
Evaluation of an effective sample prefractionation method for the proteome analysis of breast cancer tissue using narrow range two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008 Jun;72(6):1464-74. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70777. Epub 2008 Jun 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18540105
-
Proteomics of breast carcinoma.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005 Feb 5;815(1-2):215-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.11.012. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15652811 Review.
-
Advanced proteomic technologies for cancer biomarker discovery.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009 Apr;6(2):123-34. doi: 10.1586/epr.09.1. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19385940 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Proteomic Profiling of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cells. 2021 Oct 15;10(10):2768. doi: 10.3390/cells10102768. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685748 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanical cell disruption microfluidic platform based on an on-chip micropump.Biomicrofluidics. 2017 Apr 4;11(2):024112. doi: 10.1063/1.4979100. eCollection 2017 Mar. Biomicrofluidics. 2017. PMID: 28798848 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of Low-Complexity Domain Proteins FUS, EWSR1, and Their Fusions.Curr Protoc. 2025 Apr;5(4):e70136. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.70136. Curr Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40285687 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased camptothecin sensitivity of the stem-cell-like fraction of Caco2 cells correlates with an altered phosphorylation pattern of topoisomerase I.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 24;9(6):e99628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099628. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24960044 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors: what is their mechanism of action?Angiogenesis. 2010 Mar;13(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s10456-009-9160-6. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Angiogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20012482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aebersold, R. , Mann, M. , 2003. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422, 198–207. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen, P. , Hunter, T. , 2001. Oncogenic kinase signaling. Nature 411, 355–365. - PubMed
-
- Bodzon-Kulakowska, A. , Bierczynska-Krzysik, A. , Dylag, T. , Drabik, A. , Suder, P. , Noga, M. , Jarzebinska, J. , Silberring, J. , 2007. Methods for samples preparation in proteomic research. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 849, 1–31. - PubMed
-
- Carrette, O. , Burkhard, P.R. , Sanchez, J.C. , Hochstrasser, D.F. , 2006. State-of-the-art two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: a key tool of proteomics research. Nat. Protoc 1, 812–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

