The Fip35 WW domain folds with structural and mechanistic heterogeneity in molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 19383445
- PMCID: PMC2718323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.01.024
The Fip35 WW domain folds with structural and mechanistic heterogeneity in molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
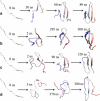
We describe molecular dynamics simulations resulting in the folding the Fip35 Hpin1 WW domain. The simulations were run on a distributed set of graphics processors, which are capable of providing up to two orders of magnitude faster computation than conventional processors. Using the Folding@home distributed computing system, we generated thousands of independent trajectories in an implicit solvent model, totaling over 2.73 ms of simulations. A small number of these trajectories folded; the folding proceeded along several distinct routes and the system folded into two distinct three-stranded beta-sheet conformations, showing that the folding mechanism of this system is distinctly heterogeneous.
Figures
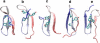
References
-
- Borrell B. Power Play. Nature. 2008;451:240–243. - PubMed
-
- Hess B., Kutzner C., van der Spoel D., Lindahl E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008;4:435–447. - PubMed
-
- Shirts M., Pande V.S. Computing - Screen savers of the world unite! Science. 2000;290:1903–1904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

