Structure of self-aggregated alamethicin in ePC membranes detected by pulsed electron-electron double resonance and electron spin echo envelope modulation spectroscopies
- PMID: 19383464
- PMCID: PMC2718270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.01.026
Structure of self-aggregated alamethicin in ePC membranes detected by pulsed electron-electron double resonance and electron spin echo envelope modulation spectroscopies
Abstract
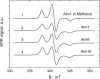
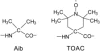
PELDOR spectroscopy was exploited to study the self-assembled super-structure of the [Glu(OMe)(7,18,19)]alamethicin molecules in vesicular membranes at peptide to lipid molar ratios in the range of 1:70-1:200. The peptide molecules were site-specifically labeled with TOAC electron spins. From the magnetic dipole-dipole interaction between the nitroxides of the monolabeled constituents and the PELDOR decay patterns measured at 77 K, intermolecular-distance distribution functions were obtained and the number of aggregated molecules (n approximately 4) was estimated. The distance distribution functions exhibit a similar maximum at 2.3 nm. In contrast to Alm16, for Alm1 and Alm8 additional maxima were recorded at 3.2 and approximately 5.2 nm. From ESEEM experiments and based on the membrane polarity profiles, the penetration depths of the different spin-labeled positions into the membrane were qualitatively estimated. It was found that the water accessibility of the spin-labels follows the order TOAC-1 > TOAC-8 approximately TOAC-16. The geometric data obtained are discussed in terms of a penknife molecular model. At least two peptide chains are aligned parallel and eight ester groups of the polar Glu(OMe)(18,19) residues are suggested to stabilize the self-aggregate superstructure.
Figures


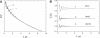

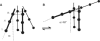
References
-
- Leitgeb B., Szekeres L., Manczinger L., Vágvölgyi C., Kredics L. The history of alamethicin: a review of the most extensively studied peptaibol. Chem. Biodivers. 2007;4:1027–1051. - PubMed
-
- Mueller P., Rudin P.O. Action potentials induced in biomolecular lipid membranes. Nature. 1968;217:713–719. - PubMed
-
- Boheim G. Statistical analysis of alamethicin in a lipid membrane. J. Membr. Biol. 1974;19:277–303. - PubMed
-
- Sansom M.S.P. Alamethicin and related peptaibols—model ion channels. Eur. Biophys. J. 1993;22:105–124. - PubMed
-
- Baumann G., Mueller P. A molecular model of membrane excitability. J. Supramol. Struct. 1974;2:538–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

