The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor promotes efferocytosis of apoptotic cells
- PMID: 19383607
- PMCID: PMC2719341
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.010066
The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor promotes efferocytosis of apoptotic cells
Abstract
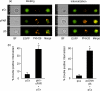
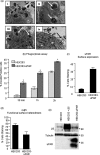
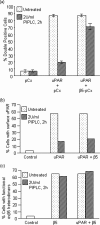
The urokinase receptor (uPAR), expressed on the surface of many cell types, coordinates plasmin-mediated cell surface proteolysis for matrix remodeling and promotes cell adhesion by acting as a binding protein for vitronectin. There is great clinical interest in uPAR in the cancer field as numerous reports have demonstrated that up-regulation of the uPA system is correlated with malignancy of various carcinomas. Using both stable cell lines overexpressing uPAR and transient gene transfer, here we provide evidence for a non-reported role of uPAR in the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, a process that has recently been termed efferocytosis. When uPAR was expressed in human embryonic kidney cells, hamster melanoma cells, or breast cancer cells (BCCs), there was a robust enhancement in the efferocytosis of apoptotic cells. uPAR-expressing cells failed to stimulate engulfment of viable cells, suggesting that uPAR enhances recognition of one or more determinant on the surface of the apoptotic cell. uPAR-mediated engulfment was not inhibited by expression of mutant beta5 integrin, nor was alphavbeta5 integrin-mediated engulfment modulated by cleavage of uPAR by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Further, we found that the more aggressive BCCs had a higher phagocytic capacity that correlated with uPAR expression and cleavage of membrane-associated uPAR in MDA-MB231 BCCs significantly impaired phagocytic activity. Because efferocytosis is critical for the resolution of inflammation and production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, overexpression of uPAR in tumor cells may promote a tolerogenic microenvironment that favors tumor progression.
Figures


References
-
- Blasi F. ( 1993) Bioessays 15, 105– 111 - PubMed
-
- Rømer J., Bugge T. H., Pyke C., Lund L. R., Flick M. J., Degen J. L., Danø K. ( 1996) Nat. Med. 2, 725. - PubMed
-
- Romer J., Bugge T. H., Pyke C., Lund L. R., Flick M. J., Degen J. L., Dano K. ( 1996) Nat. Med. 2, 287– 292 - PubMed
-
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. ( 1988) Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 4, 93– 126 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

