Characterization of six human disease-associated inversion polymorphisms
- PMID: 19383631
- PMCID: PMC2701327
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddp187
Characterization of six human disease-associated inversion polymorphisms
Abstract
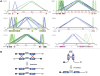
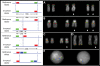
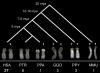
The human genome is a highly dynamic structure that shows a wide range of genetic polymorphic variation. Unlike other types of structural variation, little is known about inversion variants within normal individuals because such events are typically balanced and are difficult to detect and analyze by standard molecular approaches. Using sequence-based, cytogenetic and genotyping approaches, we characterized six large inversion polymorphisms that map to regions associated with genomic disorders with complex segmental duplications mapping at the breakpoints. We developed a metaphase FISH-based assay to genotype inversions and analyzed the chromosomes of 27 individuals from three HapMap populations. In this subset, we find that these inversions are less frequent or absent in Asians when compared with European and Yoruban populations. Analyzing multiple individuals from outgroup species of great apes, we show that most of these large inversion polymorphisms are specific to the human lineage with two exceptions, 17q21.31 and 8p23 inversions, which are found to be similarly polymorphic in other great ape species and where the inverted allele represents the ancestral state. Investigating linkage disequilibrium relationships with genotyped SNPs, we provide evidence that most of these inversions appear to have arisen on at least two different haplotype backgrounds. In these cases, discovery and genotyping methods based on SNPs may be confounded and molecular cytogenetics remains the only method to genotype these inversions.
Figures



References
-
- Iafrate A.J., Feuk L., Rivera M.N., Listewnik M.L., Donahoe P.K., Qi Y., Scherer S.W., Lee C. Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2004;36:949–951. - PubMed
-
- Sebat J., Lakshmi B., Troge J., Alexander J., Young J., Lundin P., Maner S., Massa H., Walker M., Chi M., et al. Large-scale copy number polymorphism in the human genome. Science. 2004;305:525–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

