Crystal structure of human aquaporin 4 at 1.8 A and its mechanism of conductance
- PMID: 19383790
- PMCID: PMC2678640
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0902725106
Crystal structure of human aquaporin 4 at 1.8 A and its mechanism of conductance
Abstract
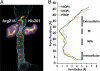
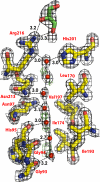
Aquaporin (AQP) 4 is the predominant water channel in the mammalian brain, abundantly expressed in the blood-brain and brain-cerebrospinal fluid interfaces of glial cells. Its function in cerebral water balance has implications in neuropathological disorders, including brain edema, stroke, and head injuries. The 1.8-A crystal structure reveals the molecular basis for the water selectivity of the channel. Unlike the case in the structures of water-selective AQPs AqpZ and AQP1, the asparagines of the 2 Asn-Pro-Ala motifs do not hydrogen bond to the same water molecule; instead, they bond to 2 different water molecules in the center of the channel. Molecular dynamics simulations were performed to ask how this observation bears on the proposed mechanisms for how AQPs remain totally insulating to any proton conductance while maintaining a single file of hydrogen bonded water molecules throughout the channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
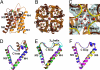
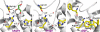

References
-
- Rojek A, Praetorius J, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S, Fenton RA. A current view of the mammalian aquaglyceroporins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:301–327. - PubMed
-
- King LS, Kozono D, Agre P. From structure to disease: The evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:687–698. - PubMed
-
- Badaut J, Brunet JF, Regli L. Aquaporins in the brain: From aqueduct to “multi-duct.”. Metab Brain Dis. 2007;22:251–263. - PubMed
-
- Manley GT, et al. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med. 2000;6:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Badaut J, Lasbennes F, Magistretti PJ, Regli L. Aquaporins in Brain: Distribution, Physiology, and Pathophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:367–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

