The indenoisoquinoline noncamptothecin topoisomerase I inhibitors: update and perspectives
- PMID: 19383846
- PMCID: PMC2888777
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0706
The indenoisoquinoline noncamptothecin topoisomerase I inhibitors: update and perspectives
Abstract
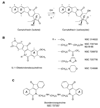
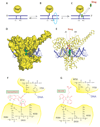
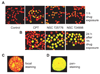
Because camptothecins are effective against previously resistant tumors and are the only class of topoisomerase I (Top1) inhibitors approved for cancer treatment, we developed the indenoisoquinolines. Like camptothecins, the indenoisoquinolines selectively trap Top1-DNA cleavage complexes and have been cocrystallized with the Top1-DNA cleavage complexes. Indenoisoquinolines show antitumor activity in animal models. They have several advantages over the camptothecins: (a) They are synthetic and chemically stable. (b) The Top1 cleavage sites trapped by the indenoisoquinolines have different genomic locations, implying differential targeting of cancer cell genomes. (c) The Top1 cleavage complexes trapped by indenoisoquinolines are more stable, indicative of prolonged drug action. (d) They are seldom or not used as substrates for the multidrug resistance efflux pumps (ABCG2 and MDR-1). Among the >400 indenoisoquinolines synthesized and evaluated, three have been retained as leads for clinical development by the National Cancer Institute: NSC 706744, NSC 725776 (Indimitecan), and NSC 724998 (Indotecan). The trapping of Top1 cleavage complexes by indenoisoquinolines in cells results in the rapid and sustained phosphorylation of histone H2AX (γ-H2AX). We discuss the use of γ-H2AX as a pharmacodynamic biomarker for the clinical development of the indenoisoquinolines.
Figures
References
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Hsiang YH, Liu LF. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988;48:1722–1726. - PubMed
-
- Giovanella BC, Stehlin JS, Wall ME, et al. DNA topoisomerase I-targeted chemotherapy of human colon cancer in xenografts. Science. 1989;246:1046–1048. - PubMed
-
- Erickson-Miller CL, May RD, Tomaszewski J, et al. Differential toxicity of camptothecin, topotecan and 9-aminocamptothecin to human, canine, and murine myeloid progenitors (CFU-GM) in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;39:467–472. - PubMed
-
- Cushman M, Cheng L. Stereoselective oxidation by thionyl chloride leading to the indeno[1,2-c]isoquinoline system. J Org Chem. 1978;43:3781–3783.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

