Arginine vasopressin regulation in pre- and postpubertal male rats by the androgen metabolite 3beta-diol
- PMID: 19383875
- PMCID: PMC2692392
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00037.2009
Arginine vasopressin regulation in pre- and postpubertal male rats by the androgen metabolite 3beta-diol
Erratum in
- Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jul;297(1):E270
Abstract
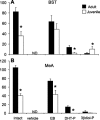
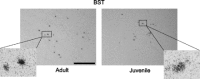
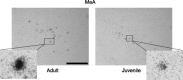
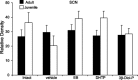
Arginine vasopressin (AVP) is a nonapeptide expressed in several brain regions. In addition to its well-characterized role in osmoregulation, AVP regulates paternal behavior, aggression,circadian rhythms, and the stress response. In the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST), AVP gene expression is tightly regulated by gonadal steroid hormones. However, the degree by which AVP is regulated by gonadal steroid hormones in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and medial amygdala (MeA) is unclear. Previous studies have shown that AVP expression in the brain of gonadectomized rats is restored with testosterone, 17beta-estradiol, and 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone(DHT) replacement. In addition, we have demonstrated that 3beta-diol, a metabolite of DHT,increased AVP promoter activity in a neuronal cell line and that the effects of 3beta-diol on AVP promoter activity were mediated by estrogen receptor-beta. To test whether 3beta-diol has a physiological role in the regulation of central AVP expression in vivo, we gonadectomized pre- and postpubertal male rats and followed with once daily injections of estradiol benzoate (EB),DHT-propionate, 3beta-diol-dipropionate, or vehicle. The SCN, BST, and MeA were analyzed for AVP mRNA expression using in situ hybridization. In the BST, intact juveniles had significantly fewer AVP-expressing cells than adults. GDX abolished all AVP mRNA expression in the BST in both age groups, whereas treatment with EB restored >80% and DHTP <10% of the AVP expression. Interestingly, 3beta-diol-proprionate was more effective at inducing AVP expression in juveniles than in adults, suggesting that the regulation of AVP by 3beta-diol might be age dependent [corrected].
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgens alter corticotropin releasing hormone and arginine vasopressin mRNA within forebrain sites known to regulate activity in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.J Neuroendocrinol. 2001 May;13(5):442-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2001.00653.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11328455
-
Estrogen receptor-beta mediates dihydrotestosterone-induced stimulation of the arginine vasopressin promoter in neuronal cells.Endocrinology. 2007 Jul;148(7):3371-82. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0086. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17412808
-
Organizational effects of testosterone, estradiol, and dihydrotestosterone on vasopressin mRNA expression in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.J Neurobiol. 2003 Feb 15;54(3):502-10. doi: 10.1002/neu.10157. J Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 12532400
-
An alternate pathway for androgen regulation of brain function: activation of estrogen receptor beta by the metabolite of dihydrotestosterone, 5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol.Horm Behav. 2008 May;53(5):741-52. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.09.012. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Horm Behav. 2008. PMID: 18067894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen modulates oxytocin gene expression in regions of the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei that contain estrogen receptor-beta.Prog Brain Res. 2002;139:15-29. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)39004-6. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12436923 Review.
Cited by
-
Oestradiol synthesized by female neurons generates sex differences in neuritogenesis.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 24;6:31891. doi: 10.1038/srep31891. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27553191 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative mapping reveals age and sex differences in vasopressin, but not oxytocin, immunoreactivity in the rat social behavior neural network.J Comp Neurol. 2017 Aug 1;525(11):2549-2570. doi: 10.1002/cne.24216. Epub 2017 May 8. J Comp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28340511 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axes: sex differences in regulation of stress responsivity.Stress. 2017 Sep;20(5):476-494. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2017.1369523. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Stress. 2017. PMID: 28859530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of human oestrogen receptor beta (ERβ) splice variants in neuronal cells.J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Oct;24(10):1311-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02337.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22577883 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-dependent effects of acute stress and alcohol exposure during adolescence on mRNA expression of brain signaling systems involved in reward and stress responses in young adult rats.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Sep 26;15(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00649-5. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 39327618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao JZ, Ni CR, Zheng WQ. Age-related effects of estrogen on the expression of estrogen receptor alpha and beta mRNA in the ovariectomized monkey hypothalamus. Neurosci Bull 22: 97–102, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Griebel G, Farrokhi C, Markham C, Yang M, Blanchard DC. AVP V1b selective antagonist SSR149415 blocks aggressive behaviors in hamsters. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80: 189–194, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Burgess LH, Handa RJ. Hormonal regulation of androgen receptor mRNA in the brain and anterior pituitary gland of the male rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 19: 31–38, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Caffe AR, van Leeuwen FW, Luiten PG. Vasopressin cells in the medial amygdala of the rat project to the lateral septum and ventral hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 261: 237–252, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

