Test-retest variability of quantitative [11C]PIB studies in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19384547
- PMCID: PMC2758198
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-009-1129-6
Test-retest variability of quantitative [11C]PIB studies in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to assess the test-retest variability of [11C]PIB studies in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and healthy controls using several tracer kinetic models and to assess the suitability of the cerebellum as reference tissue.
Methods: [11C]PIB studies with arterial sampling were performed in eight AD patients and eight healthy controls. Retest scans were performed in six controls and six AD patients. Data were analysed using plasma input and reference tissue models, together with simple ratios.
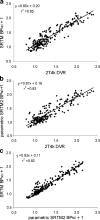
Results: Test-retest variability was best ( approximately 3%) for SRTM2, a parametric method based on the simplified reference tissue model. Highest values ( approximately 10%) were found for plasma input models. Cerebellar V(T) values did not differ significantly between AD and controls.
Conclusion: Parametric SRTM2 with the cerebellum as reference tissue is the method of choice for quantitative analysis of [11C]PIB PET studies.
Figures


References
-
- Ritchie CW, Bush AI, Mackinnon A, Macfarlane S, Mastwyk M, MacGregor L, et al. Metal-protein attenuation with iodochlorhydroxyquin (clioquinol) targeting Abeta amyloid deposition and toxicity in Alzheimer disease: a pilot phase 2 clinical trial. Arch Neurol 2003;60:1685–91. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.12.1685. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

