Movement disorder and neuronal migration disorder due to ARFGEF2 mutation
- PMID: 19384555
- PMCID: PMC2758209
- DOI: 10.1007/s10048-009-0192-2
Movement disorder and neuronal migration disorder due to ARFGEF2 mutation
Abstract
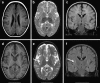
We report a child with a severe choreadystonic movement disorder, bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia (BPNH), and secondary microcephaly based on compound heterozygosity for two new ARFGEF2 mutations (c.2031_2038dup and c.3798_3802del), changing the limited knowledge about the phenotype. The brain MRI shows bilateral hyperintensity of the putamen, BPNH, and generalized atrophy. Loss of ARFGEF2 function affects vesicle trafficking, proliferation/apoptosis, and neurotransmitter receptor function. This can explain BPNH and microcephaly. We hypothesize that the movement disorder and the preferential damage to the basal ganglia, specifically to the putamen, may be caused by an increased sensitivity to degeneration, a dynamic dysfunction due to neurotransmitter receptor mislocalization or a combination of both.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The expanding phenotypic spectrum of ARFGEF2 gene mutation: Cardiomyopathy and movement disorder.Brain Dev. 2016 Jan;38(1):124-7. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Brain Dev. 2016. PMID: 26126837
-
Periventricular nodular heterotopia and dystonia due to an ARFGEF2 mutation.Pediatr Neurol. 2014 Sep;51(3):461-4. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.05.008. Epub 2014 May 15. Pediatr Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25160555
-
Elaborating the phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations in ARFGEF2: case study and literature review.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2013 Nov;17(6):666-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23755938 Review.
-
Periventricular heterotopia in 6q terminal deletion syndrome: role of the C6orf70 gene.Brain. 2013 Nov;136(Pt 11):3378-94. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt249. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Brain. 2013. PMID: 24056535
-
Cerebral organoids to unravel the mechanisms underlying malformations of human cortical development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar;111:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32741653 Review.
Cited by
-
Filamin A regulates neuronal migration through brefeldin A-inhibited guanine exchange factor 2-dependent Arf1 activation.J Neurosci. 2013 Oct 2;33(40):15735-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1939-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24089482 Free PMC article.
-
ARF1-related disorder: phenotypic and molecular spectrum.J Med Genet. 2023 Oct;60(10):999-1005. doi: 10.1136/jmg-2022-108803. Epub 2023 Apr 25. J Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37185208 Free PMC article.
-
Periventricular nodular heterotopia in a Chihuahua.J Vet Intern Med. 2020 Jul;34(4):1570-1575. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15803. Epub 2020 May 23. J Vet Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32445227 Free PMC article.
-
Cases report: MRI findings of asymptomatically familial subependymal heterotopia with filamin A gene abnormality.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 27;16:956545. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.956545. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35968360 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to environmental bisphenol A inhibits HTR-8/SVneo cell migration and invasion.J Biomed Res. 2020 Jun 30;34(5):369-378. doi: 10.7555/JBR.34.20200013. J Biomed Res. 2020. PMID: 32981897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of neural science 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2000.
-
- Charych EI, Yu W, Miralles CP, Serwanski DR, Li X, Rubio M, et al. The brefeldin A-inhibited GDP/GTP exchange factor 2, a protein involved in vesicular trafficking, interacts with the beta subunits of the GABA receptors. J Neurochem. 2004;90(1):173–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02481.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

