Targeting eEF1A by a Legionella pneumophila effector leads to inhibition of protein synthesis and induction of host stress response
- PMID: 19386084
- PMCID: PMC2967282
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01301.x
Targeting eEF1A by a Legionella pneumophila effector leads to inhibition of protein synthesis and induction of host stress response
Abstract
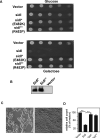
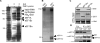
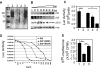
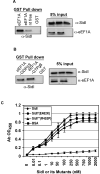
The Legionella pneumophila Dot/Icm type IV secretion system is essential for the biogenesis of a phagosome that supports bacterial multiplication, most likely via the functions of its protein substrates. Recent studies indicate that fundamental cellular processes, such as vesicle trafficking, stress response, autophagy and cell death, are modulated by these effectors. However, how each translocated protein contributes to the modulation of these pathways is largely unknown. In a screen to search substrates of the Dot/Icm transporter that can cause host cell death, we identified a gene whose product is lethal to yeast and mammalian cells. We demonstrate that this protein, called SidI, is a substrate of the Dot/Icm type IV protein transporter that targets the host protein translation process. Our results indicate that SidI specifically interacts with eEF1A and eEF1Bgamma, two components of the eukaryotic protein translation elongation machinery and such interactions leads to inhibition of host protein synthesis. Furthermore, we have isolated two SidI substitution mutants that retain the target binding activity but have lost toxicity to eukaryotic cells, suggesting potential biochemical effect of SidI on eEF1A and eEF1Bgamma. We also show that infection by L. pneumophila leads to eEF1A-mediated activation of the heat shock regulatory protein HSF1 in a virulence-dependent manner and deletion of sidI affects such activation. Moreover, similar response occurred in cells transiently transfected to express SidI. Thus, inhibition of host protein synthesis by specific effectors contributes to the induction of stress response in L. pneumophila-infected cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Legionella pneumophila Metaeffector Lpg2505 (MesI) Regulates SidI-Mediated Translation Inhibition and Novel Glycosyl Hydrolase Activity.Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00853-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00853-19. Print 2020 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32122942 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted bacterial effectors that inhibit host protein synthesis are critical for induction of the innate immune response to virulent Legionella pneumophila.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Feb;7(2):e1001289. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001289. Epub 2011 Feb 17. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21390206 Free PMC article.
-
Intrabacterial Regulation of a Cytotoxic Effector by Its Cognate Metaeffector Promotes Legionella pneumophila Virulence.mSphere. 2023 Feb 21;8(1):e0055222. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00552-22. Epub 2023 Jan 4. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 36598225 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Eukaryotic mRNA Translation by Legionella pneumophila.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Apr 29;7:80. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00080. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32411722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylating Effectors of Legionella pneumophila: Finding the Sweet Spots for Host Cell Subversion.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 4;12(2):255. doi: 10.3390/biom12020255. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of the Ankyrin H Core Effector of Legionella with the Host LARP7 Component of the 7SK snRNP Complex.mBio. 2019 Aug 27;10(4):e01942-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01942-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31455655 Free PMC article.
-
The Legionella pneumophila Metaeffector Lpg2505 (MesI) Regulates SidI-Mediated Translation Inhibition and Novel Glycosyl Hydrolase Activity.Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00853-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00853-19. Print 2020 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32122942 Free PMC article.
-
Life Stage-specific Proteomes of Legionella pneumophila Reveal a Highly Differential Abundance of Virulence-associated Dot/Icm effectors.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Jan;15(1):177-200. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.053579. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26545400 Free PMC article.
-
A new method to determine in vivo interactomes reveals binding of the Legionella pneumophila effector PieE to multiple rab GTPases.mBio. 2014 Aug 12;5(4):e01148-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01148-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25118235 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of the obligate intracellular bacterium Coxiella burnetii.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Aug;11(8):561-73. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3049. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23797173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-Zant A, Jones S, Asare R, Suttles J, Price C, Graham J, Kwaik YA. Anti-apoptotic signalling by the Dot/Icm secretion system of L. pneumophila. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:246–264. - PubMed
-
- Bardill JP, Miller JL, Vogel JP. IcmS-dependent translocation of SdeA into macrophages by the Legionella pneumophila type IV secretion system. Mol Microbiol. 2005;56:90–103. - PubMed
-
- Bec G, Kerjan P, Zha XD, Waller JP. Valyl-tRNA synthetase from rabbit liver. I. Purification as a heterotypic complex in association with elongation factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:21131–21137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

