Beyond NMR spectra of antimicrobial peptides: dynamical images at atomic resolution and functional insights
- PMID: 19386477
- PMCID: PMC2694728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2009.03.003
Beyond NMR spectra of antimicrobial peptides: dynamical images at atomic resolution and functional insights
Abstract
There is a considerable current interest in understanding the function of antimicrobial peptides for the development of potent novel antibiotic compounds with a very high selectivity. Since their interaction with the cell membrane is the major driving force for their function, solid-state NMR spectroscopy is the unique method of choice to study these insoluble, non-crystalline, membrane-peptide complexes. Here I discuss solid-state NMR studies of antimicrobial peptides that have reported high-resolution structure, dynamics, orientation, and oligomeric states of antimicrobial peptides in a membrane environment, and also address important questions about the mechanism of action at atomic-level resolution. Increasing number of solid-state NMR applications to antimicrobial peptides are expected in the near future, as these compounds are promising candidates to overcome ever-increasing antibiotic resistance problem and are well suited for the development and applications of solid-state NMR techniques.
Figures
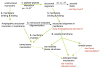
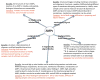
References
-
- Haeberlen U. Adv Magn Reson. Academic Press; New York: 1976. High resolution NMR in solids: selective averaging.
-
- Schmidt-Rohr K, Spiess HW. Multidimensional Solid-State NMR and Polymers. Academic Press; New York: 1994.
-
- Ramamoorthy, editor. NMR Spectroscopy of Biological Solids. Taylor & Francis; New York: 2006.
-
- Ramamoorthy A, Wei Y, Lee DK. Ann Rep NMR Spectrosc. 2004;52:1–52. Reports a comprehensive analysis of PISEMA solid-state NMR spectroscopy to study biological solids.
-
- Cross TA, Opella SJ. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994;4:574–581.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

