Introgression of apomixis into sexual species is inhibited by mentor effects and ploidy barriers in the Ranunculus auricomus complex
- PMID: 19386790
- PMCID: PMC2706732
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcp093
Introgression of apomixis into sexual species is inhibited by mentor effects and ploidy barriers in the Ranunculus auricomus complex
Abstract
Background and aims: Apomictic plants maintain functional pollen, and via pollination the genetic factors controlling apomixis can be potentially transferred to congeneric sexual populations. In contrast, the sexual individuals do not fertilize apomictic plants which produce seeds without fertilization of the egg cells. This unidirectional introgressive hybridization is expected finally to replace sexuality by apomixis and is thought to be a causal factor for the wide geographical distribution of apomictic complexes. Nevertheless, this process may be inhibited by induced selfing (mentor effects) of otherwise self-incompatible sexual individuals. Here whether mentor effects or actual cross-fertilization takes place between diploid sexual and polyploid apomictic cytotypes in the Ranunculus auricomus complex was tested via experimental crosses.
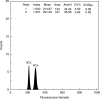
Methods: Diploid sexual mother plants were pollinated with tetra- and hexaploid apomictic pollen donators by hand, and the amount of well-developed seed compared with aborted seed was evaluated. The reproductive pathways were assessed in the well-developed seed via flow cytometric seed screen (FCSS).
Key results: The majority of seed was aborted; the well-developed seeds have resulted from both mentor effects and cross-fertilization at very low frequencies (1.3 and 1.6 % of achenes, respectively). Pollination by 4x apomictic pollen plants results more frequently in cross-fertilization, whereas pollen from 6x plants more frequently induced mentor effects.
Conclusions: It is concluded that introgression of apomixis into sexual populations is limited by ploidy barriers in the R. auricomus complex, and to a minor extent by mentor effects. In mixed populations, sexuality cannot be replaced by apomixis because the higher fertility of sexual populations still compensates the low frequencies of potential introgression of apomixis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reproductive differentiation into sexual and apomictic polyploid cytotypes in Potentilla puberula (Potentilleae, Rosaceae).Ann Bot. 2013 Oct;112(6):1159-68. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct167. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Ann Bot. 2013. PMID: 23960045 Free PMC article.
-
Ploidy-Dependent Effects of Light Stress on the Mode of Reproduction in the Ranunculus auricomus Complex (Ranunculaceae).Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 20;11:104. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00104. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32153611 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cold treatments on fitness and mode of reproduction in the diploid and polyploid alpine plant Ranunculus kuepferi (Ranunculaceae).Ann Bot. 2018 Jun 8;121(7):1287-1298. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcy017. Ann Bot. 2018. PMID: 29462249 Free PMC article.
-
The Rise of Apomixis in Natural Plant Populations.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Apr 2;10:358. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00358. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31001296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of self-fertility in apomictic plants.Sex Plant Reprod. 2010 Mar;23(1):73-86. doi: 10.1007/s00497-009-0122-3. Epub 2009 Nov 20. Sex Plant Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20165965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Breeding system of diploid sexuals within the Ranunculus auricomus complex and its role in a geographical parthenogenesis scenario.Ecol Evol. 2020 Dec 3;10(24):14435-14450. doi: 10.1002/ece3.7073. eCollection 2020 Dec. Ecol Evol. 2020. PMID: 33391726 Free PMC article.
-
A continental-wide perspective: the genepool of nuclear encoded ribosomal DNA and single-copy gene sequences in North American Boechera (Brassicaceae).PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036491. Epub 2012 May 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22606266 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomics of Southern European Taxa in the Ranunculus auricomus Species Complex: The Apple Doesn't Fall Far from the Tree.Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;12(21):3664. doi: 10.3390/plants12213664. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960021 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of apospory and bypass of meiosis via apomixis after sexual hybridisation and polyploidisation.New Phytol. 2014 Dec;204(4):1000-12. doi: 10.1111/nph.12954. Epub 2014 Jul 31. New Phytol. 2014. PMID: 25081588 Free PMC article.
-
Geographical parthenogenesis and population genetic structure in the alpine species Ranunculus kuepferi (Ranunculaceae).Heredity (Edinb). 2013 Jun;110(6):560-9. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2013.1. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Heredity (Edinb). 2013. PMID: 23403961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asker SE, Jerling L. Apomixis in plants. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1992.
-
- Bell G. The masterpiece of nature: the evolution and genetics of sexuality. Berkeley: California Press; 1982.
-
- Baker HG. Support for Baker's law – as a rule. Evolution. 1967;21:853–856. - PubMed
-
- Baker HG, Stebbins GL. The genetics of colonizing species. New York: Academic Press; 1965.
-
- Barcaccia G, Arzenton F, Sharbel TF, Varotto S, Parrini P, Lucchin M. Genetic diversity and reproductive biology in ecotypes of the facultative apomict Hypericum perforatum L. Heredity. 2006;96:322–334. - PubMed

