Polarity-sensitive modulation of cortical neurotransmitters by transcranial stimulation
- PMID: 19386916
- PMCID: PMC6665468
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4432-08.2009
Polarity-sensitive modulation of cortical neurotransmitters by transcranial stimulation
Abstract
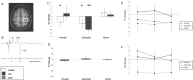
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) modulates cortical excitability and is being used for human studies more frequently. Here we probe the underlying neuronal mechanisms by measuring polarity-specific changes in neurotransmitter concentrations using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). MRS provides evidence that excitatory (anodal) tDCS causes locally reduced GABA while inhibitory (cathodal) stimulation causes reduced glutamatergic neuronal activity with a highly correlated reduction in GABA, presumably due to the close biochemical relationship between the two neurotransmitters.
Figures

References
-
- Bliss T, Collingridge G, Morris R. Oxford: Oxford UP; 2003. LTP: long-term potentiation; enhancing neuroscience for 30 years.
-
- Floyer-Lea A, Wylezinska M, Kincses T, Matthews PM. Rapid modulation of GABA concentration in human sensorimotor cortex during motor learning. J Neurophysiol. 2006;95:1639–1644. - PubMed
-
- Hendry SH, Jones EG. Activity-dependent regulation of GABA expression in the visual cortex of adult monkeys. Neuron. 1988;1:701–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
