Nuclear factor kappaB, airway epithelium, and asthma: avenues for redox control
- PMID: 19387025
- PMCID: PMC2677399
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.200806-054RM
Nuclear factor kappaB, airway epithelium, and asthma: avenues for redox control
Abstract
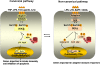
A wealth of recent studies points to the importance of airway epithelial cells in the orchestration of inflammatory responses in the allergic inflamed lung. Studies also point to a role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of chronic inflammatory diseases. This article provides a perspective on the significance of airway epithelial cells in allergic inflammation, and reviews the relevance of the transcription factor, nuclear factor kappaB, herein. We also provide the reader with a perspective on the role that oxidants can play in lung homeostasis, and address the concept of "redox biology." In addition, we review recent evidence that highlights potential inhibitory roles of oxidants on nuclear factor kappaB activation and inflammation, and discuss recent assays that have become available to probe the functional roles of oxidants in lung biology.
Figures

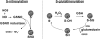


References
-
- Bousquet J, Jeffery PK, Busse WW, Johnson M, Vignola AM. Asthma: from bronchoconstriction to airways inflammation and remodeling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161:1720–1745. - PubMed
-
- Hammad H, Lambrecht BN. Dendritic cells and epithelial cells: linking innate and adaptive immunity in asthma. Nat Rev 2008;8:193–204. - PubMed
-
- Church LD, Cook GP, McDermott MF. Primer: inflammasomes and interleukin 1beta in inflammatory disorders. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2008;4:34–42. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Pantano C, Reynaert NL, van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger YM. Redox-sensitive kinases of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal 2006;8:1791–1806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
