Selenomethionine incorporation in proteins expressed in Lactococcus lactis
- PMID: 19388077
- PMCID: PMC2771314
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.97
Selenomethionine incorporation in proteins expressed in Lactococcus lactis
Abstract
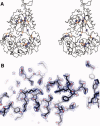
Lactococcus lactis is a promising host for (membrane) protein overproduction. Here, we describe a protocol for incorporation of selenomethionine (SeMet) into proteins expressed in L. lactis. Incorporation efficiencies of SeMet in the membrane protein complex OpuA (an ABC transporter) and the soluble protein OppA, both from L. lactis, were monitored by mass spectrometry. Both proteins incorporated SeMet with high efficiencies (>90%), which greatly extends the usefulness of the expression host L. lactis for X-ray crystallography purposes. The crystal structure of ligand-free OppA was determined at 2.4 A resolution by a semiautomatic approach using selenium single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kinetics and consequences of binding of nona- and dodecapeptides to the oligopeptide binding protein (OppA) of Lactococcus lactis.Biochemistry. 1999 Nov 2;38(44):14440-50. doi: 10.1021/bi9914715. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10545166
-
Single-molecule studies of conformational states and dynamics in the ABC importer OpuA.FEBS Lett. 2021 Mar;595(6):717-734. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14026. Epub 2021 Jan 6. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 33314056
-
Specificity and selectivity determinants of peptide transport in Lactococcus lactis and other microorganisms.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Aug;57(3):640-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04698.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16045610 Review.
-
Structure of the multidrug ABC transporter Sav1866 from Staphylococcus aureus in complex with AMP-PNP.FEBS Lett. 2007 Mar 6;581(5):935-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.073. Epub 2007 Feb 7. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17303126
-
Multidrug transporters and antibiotic resistance in Lactococcus lactis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Sep 10;1555(1-3):1-7. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(02)00246-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12206883 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the Redox Biology of Selenium in the Search of Targeted Cancer Therapies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 May 13;9(5):420. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050420. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32414091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structural basis for peptide selection by the transport receptor OppA.EMBO J. 2009 May 6;28(9):1332-40. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.65. Epub 2009 Mar 19. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19300437 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the vitamin B3 transporter PnuC, a full-length SWEET homolog.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Nov;21(11):1013-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2909. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25291599
-
Mechanistic insights into staphylopine-mediated metal acquisition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 10;115(15):3942-3947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718382115. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29581261 Free PMC article.
-
pH- and Temperature-Dependent Peptide Binding to the Lactococcus lactis Oligopeptide-Binding Protein A Measured with a Fluorescence Anisotropy Assay.ACS Omega. 2019 Feb 28;4(2):2812-2822. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b02427. Epub 2019 Feb 6. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 30842982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geertsma ER, Poolman B. High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria. Nat Methods. 2007;4:705–707. - PubMed
-
- Morello E, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Llull D, Solé V, Miraglio N, Langella P, Poquet I. Lactococcus lactis, an efficient cell factory for recombinant protein production and secretion. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;14:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Kunji ERS, Slotboom DJ, Poolman B. Lactococcus lactis as host for overproduction of functional membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1610:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Kunji ERS, Chan KW, Slotboom DJ, Floyd S, O'Connor R, Monné M. Eukaryotic membrane protein overproduction in Lactococcus lactis. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005;16:546–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

