MRI methods for evaluating the effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitor administration used to enhance chemotherapy efficiency in a breast tumor xenograft model
- PMID: 19388114
- PMCID: PMC4511711
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21737
MRI methods for evaluating the effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitor administration used to enhance chemotherapy efficiency in a breast tumor xenograft model
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate whether quantitative MRI parameters are sensitive to the effects of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib and can discriminate between two different treatment protocols.
Materials and methods: Untreated mice with BT474 breast tumor xenografts were characterized in a preliminary study. Subsequently, tumor volume, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), transendothelial permeability (K(ps)), and fractional plasma volume (fPV) were measured in three groups of mice receiving: 1) control vehicle for 10 days, or gefitinib as 2) a single daily dose for 10 days or 3) a 2-day pulsed dose.
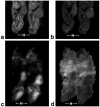
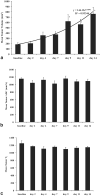
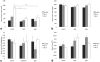
Results: Gefitinib treatment resulted in significant tumor growth inhibition (pulsed: 439 +/- 93; daily: 404 +/- 53; control: 891 +/- 174 mm(3), P < 0.050) and lower cell density (pulsed: 0.15 +/- 0.01, daily: 0.17 +/- 0.01, control: 0.24 +/- 0.01, P < 0.050) after 9 days. Tumor ADC increased in treated groups but decreased in controls (P > 0.050). Tumor K(ps) decreased with pulsed treatment but rebounded afterwards and increased with daily treatment (P > 0.050). Tumor fPV increased in both treated groups, decreasing afterwards with pulsed treatment (P > 0.050).
Conclusion: Quantitative MRI can provide a sensitive measure of gefitinib-induced tumor changes, potentially distinguish between treatment regimens, and may be useful for determining optimal treatment scheduling for enhancing chemotherapy delivery.
Figures




References
-
- Yarden Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. Signaling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(Suppl 4):3–8. - PubMed
-
- Rose-Hellekant TA, Sandgren EP. Transforming growth factor alpha- and c-myc-induced mammary carcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Nature. 2000;19:1092–1096. - PubMed
-
- Ellis LM. Epidermal growth factor receptor in tumor angiogenesis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004;18:1007–1021. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Yarmand-Bagheri R. The role of HER2 in angiogenesis. Semin Oncol. 2001;28(5 Suppl 16):27–32. - PubMed
-
- Moasser MM, Basso A, Averbuch SD, Rosen N. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (“Iressa”) inhibits HER2-driven signaling and suppresses the growth of HER2-overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7184–7188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

