Effect of inositol hexaphosphate on the development of UVB-induced skin tumors in SKH1 hairless mice
- PMID: 19389306
- PMCID: PMC2703150
Effect of inositol hexaphosphate on the development of UVB-induced skin tumors in SKH1 hairless mice
Erratum in
- Comp Med. 2009 Jun;59(3):220
Abstract
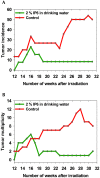
Inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) is a naturally occurring polyphosphorylated carbohydrate that is abundant in many plants and in various high-fiber foods, such as cereals and legumes. IP6 has a striking, broad-spectrum anticancer activity in various in vitro and animal models, in which it interferes with key pathways in malignancy to inhibit cell proliferation, cell-cycle progression, metastasis, invasion, and angiogenesis and to induce apoptosis. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of IP6 in drinking water on the incidence of UVB-induced skin cancer in the SKH1 (Crl: SKH1-hr) mouse model. One group of 15 mice received 2% IP6 in drinking water and UVB exposure, and the other group (n = 15) received UVB exposure only. All mice in both groups were fed an IP6-deficient diet (AIN 76A). The treatment group started receiving 2% IP6 in the drinking water 3 d before irradiation. Mice were irradiated 3 times each week, starting at a dose of 1.5 kJ/m2, with weekly increases in increments of 1.5 kJ/m2 to a final dose of 7.5 kJ/m2. Tumor formation was monitored until the week 31. IP6 in drinking water significantly decreased tumor incidence by 5-fold and tumor multiplicity by 4-fold. These results show that IP6 has an antiphotocarcinogenic effect and can protect against UVB-induced tumor formation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protective effect of inositol hexaphosphate against UVB damage in HaCaT cells and skin carcinogenesis in SKH1 hairless mice.Comp Med. 2011 Feb;61(1):39-44. Comp Med. 2011. PMID: 21819680 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of pure inositol hexaphosphate and high-bran diet in the prevention of DMBA-induced rat mammary carcinogenesis.Nutr Cancer. 1997;28(1):7-13. doi: 10.1080/01635589709514546. Nutr Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9200144
-
Cancer inhibition by inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) and inositol: from laboratory to clinic.J Nutr. 2003 Nov;133(11 Suppl 1):3778S-3784S. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.11.3778S. J Nutr. 2003. PMID: 14608114 Review.
-
In vivo suppression of hormone-refractory prostate cancer growth by inositol hexaphosphate: induction of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jan 1;10(1 Pt 1):244-50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-1080-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 14734476
-
Prostate cancer and inositol hexaphosphate: efficacy and mechanisms.Anticancer Res. 2005 Jul-Aug;25(4):2891-903. Anticancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16080543 Review.
Cited by
-
Broad Spectrum Anticancer Activity of Myo-Inositol and Inositol Hexakisphosphate.Int J Endocrinol. 2016;2016:5616807. doi: 10.1155/2016/5616807. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Int J Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27795708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of inositol hexaphosphate against UVB damage in HaCaT cells and skin carcinogenesis in SKH1 hairless mice.Comp Med. 2011 Feb;61(1):39-44. Comp Med. 2011. PMID: 21819680 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Hexaphosphate (IP6) and Colon Cancer: From Concepts and First Experiments to Clinical Application.Molecules. 2020 Dec 15;25(24):5931. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245931. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33333775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Processed Panax ginseng, Sun Ginseng on UVB-irradiated Human Skin Keratinocyte and Human Dermal Fibroblast.J Ginseng Res. 2012 Jan;36(1):68-77. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2012.36.1.68. J Ginseng Res. 2012. PMID: 23717106 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in cellular levels of inositol polyphosphates during apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Dec;345(1-2):61-8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0560-0. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20725767
References
-
- Arnold JT, Wilkinson BP, Sharma S, Steele VE. 1995. Evaluation of chemopreventive agents in different mechanistic classes using a rat epithelial cell culture transformation assay. Cancer Res 55:537–543 - PubMed
-
- Babich H, Borenfreund E, Stern A. 1993. Comparative cytotoxicities of selected minor dietary non-nutrients with chemopreventive properties. Cancer Lett 73:127–133 - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. 1996. NFκB. Ten years after. Cell 87:13–20 - PubMed
-
- Bair WB, 3rd, Hart N, Einspahr J, Liu G, Dong Z, Alberts D, Bowden GT. 2002. Inhibitory effects of sodium salicylate and acetylsalicylic acid on UVB-induced mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:1645–1652 - PubMed
-
- Baten A, Ullah A, Tomazic VJ, Shamsuddin AM. 1989. Inositol-phosphate–induced enhancement of natural killer cell activity correlates with tumor suppression. Carcinogenesis 10:1595–1598 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
