Genome-wide association study of electrocardiographic conduction measures in an isolated founder population: Kosrae
- PMID: 19389651
- PMCID: PMC2673462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.02.022
Genome-wide association study of electrocardiographic conduction measures in an isolated founder population: Kosrae
Abstract
Background: Cardiac conduction, as assessed by electrocardiographic PR interval and QRS duration, is an important electrophysiological trait and a determinant of arrhythmia risk.
Objective: We sought to identify common genetic determinants of these measures.
Methods: We examined 1604 individuals from the island of Kosrae, Federated States of Micronesia, an isolated founder population. We adjusted for covariates and estimated the heritability of quantitative electrocardiographic QRS duration and PR interval and, secondarily, its subcomponents, P-wave duration and PR segment. Finally, we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in a subset of 1262 individuals genotyped using the Affymetrix GeneChip Human Mapping 500K microarray.
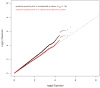
Results: The heritability of PR interval was 34% (standard error [SE] 5%, P = 4 x 10(-18)); of PR segment, 31% (SE 6%, P = 3.2 x 10(-13)); and of P-wave duration, 17% (SE 5%, P = 5.8 x 10(-6)), but the heritablility of QRS duration was only 3% (SE 4%, P = .20). Hence, GWAS was performed only for the PR interval and its subcomponents. A total of 338,049 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) passed quality filters. For the PR interval, the most significantly associated SNPs were located in and downstream of the alpha-subunit of the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel gene SCN5A, with a 4.8 ms (SE 1.0) or 0.23 standard deviation increase in adjusted PR interval for each minor allele copy of rs7638909 (P = 1.6 x 10(-6), minor allele frequency 0.40). These SNPs were also associated with P-wave duration (P = 1.5 x 10(-4)) and PR segment (P = .01) but not with QRS duration (P > or =.22).
Conclusions: The PR interval and its subcomponents showed substantial heritability in a South Pacific islander population and were associated with common genetic variation in SCN5A.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None
Figures
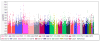


Comment in
-
The heritable nature of the electrocardiogram: How far can population genetics go?Heart Rhythm. 2009 May;6(5):642-3. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.03.007. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Heart Rhythm. 2009. PMID: 19389652 No abstract available.
References
-
- Platonov PG. Interatrial conduction in the mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: from anatomy to cardiac signals and new treatment modalities. Europace. 2007;9(Suppl 6):vi10–vi16. - PubMed
-
- Kashani A, Barold SS. Significance of QRS complex duration in patients with heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2005;46(12):2183–2192. - PubMed
-
- Moller P, Heiberg A, Berg K. The atrioventricular conduction time - a heritable trait? III. Twin studies. Clin Genet. 1982;21(3):181–183. - PubMed
-
- Havlik RJ, Garrison RJ, Fabsitz R, et al. Variability of heart rate, P–R, QRS and Q–T durations in twins. J Electrocardiol. 1980;13(1):45–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

