Target gene specificity of USF-1 is directed via p38-mediated phosphorylation-dependent acetylation
- PMID: 19389701
- PMCID: PMC2707245
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808605200
Target gene specificity of USF-1 is directed via p38-mediated phosphorylation-dependent acetylation
Abstract
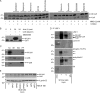
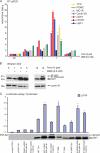
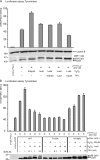
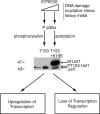
How transcription factors interpret the output from signal transduction pathways to drive distinct programs of gene expression is a key issue that underpins development and disease. The ubiquitously expressed basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper upstream stimulating factor-1 binds E-box regulatory elements (CANNTG) to regulate a wide number of gene networks. In particular, USF-1 is a key component of the tanning process. Following UV irradiation, USF-1 is phosphorylated by the p38 stress-activated kinase on threonine 153 and directly up-regulates expression of the POMC, MC1R, TYR, TYRP-1 and DCT genes. However, how phosphorylation on Thr-153 might affect the activity of USF-1 is unclear. Here we show that, in response to DNA damage, oxidative stress and cellular infection USF-1 is acetylated in a phospho-Thr-153-dependent fashion. Phospho-acetylated USF-1 is nuclear and interacts with DNA but displays altered gene regulatory properties. Phospho-acetylated USF-1 is thus proposed to be associated with loss of transcriptional activation properties toward several target genes implicated in pigmentation process and cell cycle regulation. The identification of this critical stress-dependent USF-1 modification gives new insights into understanding USF-1 gene expression modulation associated with cancer development.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

