Thrombin and interleukin-1beta decrease HOX gene expression in human first trimester decidual cells: implications for pregnancy loss
- PMID: 19389728
- PMCID: PMC2722817
- DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gap030
Thrombin and interleukin-1beta decrease HOX gene expression in human first trimester decidual cells: implications for pregnancy loss
Abstract
Bleeding or inflammation in early pregnancy may result in pregnancy loss or defective implantation. Their effect on HOX gene expression in first trimester decidua is unknown. Bleeding results in thrombin generation, although infection or inflammation results in production of cytokines typified by Interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta). First trimester decidual cells were pretreated with 17beta estradiol (E(2)), medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) or both and subsequently treated with thrombin or IL-1beta. Affymetrix microarray analysis was used to assess the expression of all HOX genes and confirmed using real-time RT-PCR. E(2) or MPA treatment resulted in significant increases in HOXA10 and HOXA11. Subsequent treatment with thrombin resulted in diminished expression of HOXA10 and HOXA9. Treatment with IL-1beta resulted in decreased expression of HOXA1, 3, 9, 10 and 11. HOXA10 expression was reduced by 70% after thrombin treatment (P = 0.018) and by 90% after IL-1beta treatment (P = 0.004). HOXA11 mRNA expression was decreased by 88% after IL-1beta treatment (P < 0.001), but not by thrombin treatment. Decidua was collected at the time of elective termination of pregnancy (n = 10) or surgical treatment of spontaneous pregnancy loss (n = 10). Real-time PCR and western analysis demonstrated decreased HOXA10 and HOXA11 RNA and protein expression in the decidua of spontaneous pregnancy loss compared with that of viable pregnancies. In conclusion, multiple HOX genes are expressed in decidual cells and inhibited by thrombin and IL-1beta. Since HOXA10 and HOXA11 are known to be necessary for successful pregnancy, these findings suggest a molecular mechanism by which bleeding or inflammation may affect pregnancy outcome.
Figures
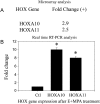

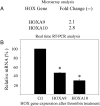

References
-
- Akbas GE, Taylor HS. HOXC and HOXD gene expression in human endometrium: lack of redundancy with HOXA paralogs. Biol Reprod. 2004;70:39–45. - PubMed
-
- Arcuri F, Buchwalder L, Toti P, Cintorino M, Tosi P, Lockwood CJ, Rybalov B, Schatz F. Differential regulation of colony stimulating factor 1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression by inflammatory cytokines in term human decidua: implications for macrophage trafficking at the fetal-maternal interface. Biol Reprod. 2007;76:433–439. - PubMed
-
- Bagot CN, Troy PJ, Taylor HS. Alteration of maternal Hoxa10 expression by in vivo gene transfection affects implantation. Gene Ther. 2000;7:1378–1384. - PubMed
-
- Benson GV, Lim H, Paria BC, Satokata I, Dey SK, Maas RL. Mechanisms of reduced fertility in Hoxa-10 mutant mice: uterine homeosis and loss of maternal Hoxa-10 expression. Development. 1996;122:2687–2696. - PubMed
-
- Block K, Kardana A, Igarashi P, Taylor HS. In utero diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure alters Hox gene expression in the developing mullerian system. FASEB J. 2000;14:1101–1108. - PubMed

