Expression of the sarA family of genes in different strains of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 19389785
- PMCID: PMC2888119
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.027417-0
Expression of the sarA family of genes in different strains of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
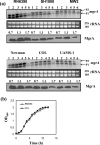
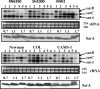
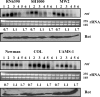
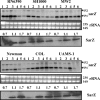
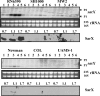
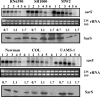
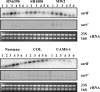
Expression of genes involved in the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus is controlled by global regulatory loci, including two-component regulatory systems and transcriptional regulators. The staphylococcal-specific SarA family of transcription regulators control large numbers of target genes involved in virulence, autolysis, biofilm formation, stress responses and metabolic processes, and are recognized as potential therapeutic targets. Expression of some of these important regulators has been examined, mostly in laboratory strains, while the pattern of expression of these genes in other strains, especially clinical isolates, is largely unknown. In this report, a comparative analysis of 10 sarA-family genes was conducted in six different S. aureus strains, including two laboratory (RN6390, SH1000) and four clinical (MW2, Newman, COL and UAMS-1) strains, by Northern and Western blot analyses. Transcription of most of the sarA-family genes showed a strong growth phase-dependence in all strains tested. Among these genes, no difference was observed in expression of the sarA, sarV, sarT and sarU genes, while a major difference was observed in expression of the sarX gene only in strain RN6390. Expression of mgrA, rot, sarZ, sarR and sarS was observed in all strains, but the level of expression varied from strain to strain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of SarX, a negative regulator of agr and exoprotein synthesis, is activated by MgrA in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jun;188(12):4288-99. doi: 10.1128/JB.00297-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16740935 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sarV (SA2062), a new transcriptional regulator, is repressed by SarA and MgrA (SA0641) and involved in the regulation of autolysis in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(16):5267-80. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.16.5267-5280.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15292128 Free PMC article.
-
sarZ, a sarA family gene, is transcriptionally activated by MgrA and is involved in the regulation of genes encoding exoproteins in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2009 Mar;191(5):1656-65. doi: 10.1128/JB.01555-08. Epub 2008 Dec 19. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19103928 Free PMC article.
-
Global regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus by the SarA protein family.Front Biosci. 2002 Aug 1;7:d1825-42. doi: 10.2741/A882. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 12133812 Review.
-
The SarA protein family of Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(3):355-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.10.032. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18083623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global analysis of transcriptional regulators in Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 26;14:126. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-126. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23442205 Free PMC article.
-
Control of thioredoxin reductase gene (trxB) transcription by SarA in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jan;192(1):336-45. doi: 10.1128/JB.01202-09. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 19854896 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of the NorB efflux pump in the adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to growth at acid pH and in resistance to moxifloxacin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Jul;55(7):3214-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00289-11. Epub 2011 May 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21555767 Free PMC article.
-
RNAIII of the Staphylococcus aureus agr system activates global regulator MgrA by stabilizing mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 10;112(45):14036-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1509251112. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26504242 Free PMC article.
-
A defense-offense multi-layered regulatory switch in a pathogenic bacterium.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 18;43(3):1357-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv001. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25628364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekshun, M. N., Levy, S. B., Mealy, T. R., Seaton, B. A. & Head, J. F. (2001). The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 Å resolution. Nat Struct Biol 8, 710–714. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T., Takeuchi, F., Kuroda, M., Yuzawa, H., Aoki, K., Oguchi, A., Nagal, Y., Iwama, N., Asano, K. & other authors (2002). Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359, 1819–1827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

