The progesterone receptor coactivator Hic-5 is involved in the pathophysiology of endometriosis
- PMID: 19389829
- PMCID: PMC2717860
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-0008
The progesterone receptor coactivator Hic-5 is involved in the pathophysiology of endometriosis
Abstract
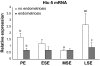
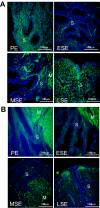
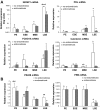
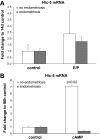
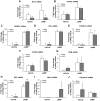
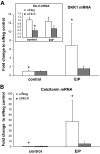
Endometriosis is an estrogen-dependent disorder primarily associated with pelvic pain and infertility in up to 10% of women of reproductive age. Recent studies suggest that resistance to progesterone action may contribute to the development and pathophysiology of this disorder. In this study we examined the in vivo and in vitro expression and function of one progesterone receptor (PR) coactivator, Hic-5, in human endometrium and endometrial stromal fibroblasts (hESFs) from 29 women with and 30 (control) women without endometriosis. Hic-5 was highly expressed in stromal, but not epithelial, cells in women without endometriosis, in a cycle-dependent manner. In contrast, Hic-5 expression was not regulated during the menstrual cycle in hESFs from women with endometriosis and was significantly reduced in hESFs from women with vs. without disease. Hic-5 mRNA expression throughout the cycle in endometrium from control women, but not those with endometriosis, correlated with expression of PR. Hic-5 mRNA in hESFs was significantly up-regulated in control but not endometriosis hESFs after treatment in vitro with 8-bromoadenosine-cAMP for 96 h but only modestly after 14 d of progesterone treatment. Hic-5 silencing did not influence cAMP-regulated gene expression but affected genes regulated solely by progesterone (e.g. DKK1 and calcitonin). Together the data suggest that the proposed progesterone resistance in endometrium from women with endometriosis derives, in part, from impaired expression of the PR coactivator, Hic-5, in endometrial tissue and cultured endometrial stromal fibroblasts.
Figures
References
-
- Eskenazi B, Warner ML 1997 Epidemiology of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 24:235–258 - PubMed
-
- Zeitoun KM, Bulun SE 1999 Aromatase: a key molecule in the pathophysiology of endometriosis and a therapeutic target. Fertil Steril 72:961–969 - PubMed
-
- Kitawaki J, Kado N, Ishihara H, Koshiba H, Kitaoka Y, Honjo H 2002 Endometriosis: the pathophysiology as an estrogen-dependent disease. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:149–155 - PubMed
-
- Burney RO, Talbi S, Hamilton AE, Vo KC, Nyegaard M, Nezhat CR, Lessey BA, Giudice LC 2007 Gene expression analysis of endometrium reveals progesterone resistance and candidate susceptibility genes in women with endometriosis. Endocrinology 148:3814–3826 - PubMed
-
- Bulun SE, Cheng YH, Yin P, Imir G, Utsunomiya H, Attar E, Innes J, Julie Kim J 2006 Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: link to failure to metabolize estradiol. Mol Cell Endocrinol 248:94–103 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

