HNF1B mutations associate with hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting
- PMID: 19389850
- PMCID: PMC2678044
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008060633
HNF1B mutations associate with hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting
Abstract
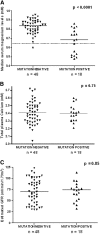
Mutations in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1B (HNF1B), which is a transcription factor expressed in tissues including renal epithelia, associate with abnormal renal development. While studying renal phenotypes of children with HNF1B mutations, we identified a teenager who presented with tetany and hypomagnesemia. We retrospectively reviewed radiographic and laboratory data for all patients from a single center who had been screened for an HNF1B mutation. We found heterozygous mutations in 21 (23%) of 91 cases of renal malformation. All mutation carriers had abnormal fetal renal ultrasonography. Plasma magnesium levels were available for 66 patients with chronic kidney disease (stages 1 to 3). Striking, 44% (eight of 18) of mutation carriers had hypomagnesemia (<1.58 mg/dl) compared with 2% (one of 48) of those without mutations (P < 0.0001). The median plasma magnesium was significantly lower among mutation carriers than those without mutations (1.68 versus 2.02 mg/dl; P < 0.0001). Because hypermagnesuria and hypocalciuria accompanied the hypomagnesemia, we analyzed genes associated with hypermagnesuria and detected highly conserved HNF1 recognition sites in FXYD2, a gene that can cause autosomal dominant hypomagnesemia and hypocalciuria when mutated. Using a luciferase reporter assay, we demonstrated HNF1B-mediated transactivation of FXYD2. These results extend the phenotype of HNF1B mutations to include hypomagnesemia. HNF1B regulates transcription of FXYD2, which participates in the tubular handling of Mg(2+), thus describing a role for HNF1B not only in nephrogenesis but also in the maintenance of tubular function.
Figures


References
-
- Murphy R, Ellard S, Hattersley AT: Clinical implications of a molecular genetic classification of monogenic beta-cell diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4: 200–213, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Maestro MA, Cardalda C, Boj SF, Luco RF, Servitja JM, Ferrer J: Distinct roles of HNF1beta, HNF1alpha, and HNF4alpha in regulating pancreas development, beta-cell function and growth. Endocr Dev 12: 33–45, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Edghill EL, Bingham C, Slingerland AS, Minton JA, Noordam C, Ellard S, Hattersley AT: Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta mutations cause neonatal diabetes and intrauterine growth retardation: Support for a critical role of HNF-1 beta in human pancreatic development. Diabet Med 23: 1301–1306, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Coffinier C, Barra J, Babinet C, Yaniv M: Expression of the vHNF1/HNF1beta homeoprotein gene during mouse organogenesis. Mech Dev 89: 211–213, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Kolatsi-Joannou M, Bingham C, Ellard S, Bulman MP, Allen LI, Hattersley AT, Woolf AS: Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta: A new kindred with renal cysts and diabetes and gene expression in normal human development. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 2175–2180, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

