Transcriptional reprogramming of gene expression in bovine somatic cell chromatin transfer embryos
- PMID: 19393066
- PMCID: PMC2695822
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-190
Transcriptional reprogramming of gene expression in bovine somatic cell chromatin transfer embryos
Abstract
Background: Successful reprogramming of a somatic genome to produce a healthy clone by somatic cells nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a rare event and the mechanisms involved in this process are poorly defined. When serial or successive rounds of cloning are performed, blastocyst and full term development rates decline even further with the increasing rounds of cloning. Identifying the "cumulative errors" could reveal the epigenetic reprogramming blocks in animal cloning.
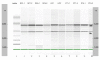
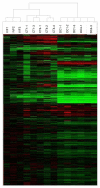
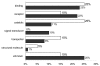
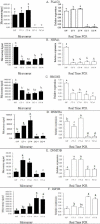
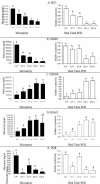
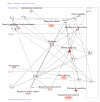
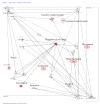
Results: Bovine clones from up to four generations of successive cloning were produced by chromatin transfer (CT). Using Affymetrix bovine microarrays we determined that the transcriptomes of blastocysts derived from the first and the fourth rounds of cloning (CT1 and CT4 respectively) have undergone an extensive reprogramming and were more similar to blastocysts derived from in vitro fertilization (IVF) than to the donor cells used for the first and the fourth rounds of chromatin transfer (DC1 and DC4 respectively). However a set of transcripts in the cloned embryos showed a misregulated pattern when compared to IVF embryos. Among the genes consistently upregulated in both CT groups compared to the IVF embryos were genes involved in regulation of cytoskeleton and cell shape. Among the genes consistently upregulated in IVF embryos compared to both CT groups were genes involved in chromatin remodelling and stress coping.
Conclusion: The present study provides a data set that could contribute in our understanding of epigenetic errors in somatic cell chromatin transfer. Identifying "cumulative errors" after serial cloning could reveal some of the epigenetic reprogramming blocks shedding light on the reprogramming process, important for both basic and applied research.
Figures



References
-
- Memili E, First NL. Zygotic and embryonic gene expression in cow: a review of timing and mechanisms of early gene expression as compared with other species. Zygote. 2000;8:87–96. - PubMed
-
- Whitworth K, Springer GK, Forrester LJ, Spollen WG, Ries J, Lamberson WR, Bivens N, Murphy CN, Mathialagan N, Green JA, et al. Developmental expression of 2489 gene clusters during pig embryogenesis: an expressed sequence tag project. Biol Reprod. 2004;71:1230–1243. - PubMed
-
- Latham KE, Schultz RM. Embryonic genome activation. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D748–759. - PubMed
-
- Han YM, Kang YK, Koo DB, Lee KK. Nuclear reprogramming of cloned embryos produced in vitro. Theriogenology. 2003;59:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Vajta G, Gjerris M. Science and technology of farm animal cloning: state of the art. Anim Reprod Sci. 2006;92:211–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

