Repetitive DNA elements, nucleosome binding and human gene expression
- PMID: 19393174
- PMCID: PMC2921533
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.01.013
Repetitive DNA elements, nucleosome binding and human gene expression
Abstract
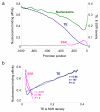
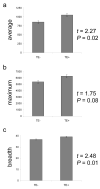
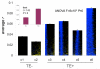
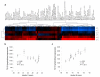
We evaluated the epigenetic contributions of repetitive DNA elements to human gene regulation. Human proximal promoter sequences show distinct distributions of transposable elements (TEs) and simple sequence repeats (SSRs). TEs are enriched distal from transcriptional start sites (TSSs) and their frequency decreases closer to TSSs, being largely absent from the core promoter region. SSRs, on the other hand, are found at low frequency distal to the TSS and then increase in frequency starting approximately 150 bp upstream of the TSS. The peak of SSR density is centered around the -35 bp position where the basal transcriptional machinery assembles. These trends in repetitive sequence distribution are strongly correlated, positively for TEs and negatively for SSRs, with relative nucleosome binding affinities along the promoters. Nucleosomes bind with highest probability distal from the TSS and the nucleosome binding affinity steadily decreases reaching its nadir just upstream of the TSS at the same point where SSR frequency is at its highest. Promoters that are enriched for TEs are more highly and broadly expressed, on average, than promoters that are devoid of TEs. In addition, promoters that have similar repetitive DNA profiles regulate genes that have more similar expression patterns and encode proteins with more similar functions than promoters that differ with respect to their repetitive DNA. Furthermore, distinct repetitive DNA promoter profiles are correlated with tissue-specific patterns of expression. These observations indicate that repetitive DNA elements mediate chromatin accessibility in proximal promoter regions and the repeat content of promoters is relevant to both gene expression and function.
Figures



References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azuaje F, Wang H, Bodenreider O. Onotlogy-driven similarity approaches to supporting gene functional assessment. Proc ISMB SIG meeting on Bio-ontologies. 2005;2005:9–10.
-
- Bejerano G, Lowe CB, Ahituv N, King B, Siepel A, Salama SR, Rubin EM, Kent WJ, Haussler D. A distal enhancer and an ultraconserved exon are derived from a novel retroposon. Nature. 2006;441:87–90. - PubMed
-
- Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:1097–101. - PubMed
-
- Britten RJ, Kohne DE. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968;161:529–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

