Peroxynitrite-induced p38 MAPK pro-apoptotic signaling in enterocytes
- PMID: 19393619
- PMCID: PMC2757937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.091
Peroxynitrite-induced p38 MAPK pro-apoptotic signaling in enterocytes
Abstract
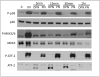
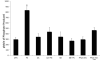
Enterocyte apoptosis in necrotizing enterocolitis is partly due to the elaboration of toxic intermediates of nitric oxide (NO), such as peroxynitrite (PN). Because p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and serine-threonine kinase (AKT) are well-characterized pro- and anti-apoptotic mediators, respectively, we hypothesized that PN could induce enterocyte apoptosis via activation of p38 and deactivation of AKT. To test this hypothesis, the rat intestinal cell line, IEC-6, was treated with PN. PN caused phosphorylation of p38, its upstream activator, MKK3/6, and downstream effector, transcription factor ATF-2. PN-induced apoptosis was inhibited by the p38 inhibitor, SB202190, and by p38 siRNA. PN decreased AKT phosphorylation; this effect was abrogated by pre-treatment with SB202190 or p38 siRNA. PN exposure also increased the activity of the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). These data demonstrate that PN-mediated apoptosis depends on the p38 pathway and that p38 mediates deactivation of AKT survival pathways possibly by the involvement of PP2A.
Figures

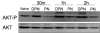
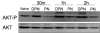
References
-
- Hackam DJ, Upperman JS, Grishin A, Ford HR. Disordered enterocyte signaling and intestinal barrier dysfunction in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2005;14:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Guner YS, Chokshi N, Petrosyan M, Upperman JS, Ford HR, Grikscheit TC. Necrotizing enterocolitis--bench to bedside: novel and emerging strategies. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2008;17:255–65. - PubMed
-
- Ford HR. Mechanism of nitric oxide-mediated intestinal barrier failure: insight into the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:294–9. - PubMed
-
- Upperman JS, Potoka D, Grishin A, Hackam D, Zamora R, Ford HR. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-mediated intestinal barrier failure in necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2005;14:159–66. - PubMed
-
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. Faseb J. 1992;6:3051–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

