Epidemiology and risk factors for thromboembolic complications of childhood nephrotic syndrome: a Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium (MWPNC) study
- PMID: 19394032
- PMCID: PMC3685482
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.01.070
Epidemiology and risk factors for thromboembolic complications of childhood nephrotic syndrome: a Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium (MWPNC) study
Abstract
Objectives: To identify clinical variables predictive of the risk of thromboembolism (TE), and to confirm the incidence of TE in primary and secondary childhood nephrotic syndrome (NS).
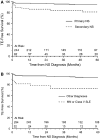
Study design: A comprehensive chart review identified 326 children with NS from any cause evaluated between 1999 and 2006. These patients had a total of 1472.8 patient-years of follow-up. Comparison statistics, survival analysis, and logistic regression were used to define TE epidemiology and clinical risk factors.
Results: We found that 9.2% of our cohort had experienced at least 1 TE. The overall incidence was 20.4 patients with TEs/1000 patient-years. The median time to the first TE was 70.5 days after diagnosis of NS. Deep venous thrombosis was the most common TE (76%) and was frequently associated with the use of a central venous catheter (45%). Significant independent predictors of TE included age > or = 12 years at onset of NS (P < .0001), severity of proteinuria (P < .0001), and history of TE preceding diagnosis of NS (P < .0001). Life- or limb-threatening TEs represented 23.7% of the events.
Conclusions: Children with NS should be carefully followed for TE, particularly those who are age 12 years or older, have severe proteinuria, or have a previous history of TE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Nephrosis and clots.J Pediatr. 2009 Jul;155(1):A2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.05.021. J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19559282 No abstract available.
References
-
- Valentini RP, Smoyer WE. Nephrotic syndrome. In: Kher KK, Schnaper HW, Makker SP, editors. Clinical Pediatric Nephrology. 2nd. London: Informa Healthcare; 2006. pp. 155–94.
-
- Eddy AA, Symons JM. Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet. 2003;362:629–39. - PubMed
-
- Orth SR, Ritz E. The nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1202–11. - PubMed
-
- Zaffanello M, Franchini M. Thromboembolism in childhood nephrotic syndrome: a rare but serious complication. Hematology. 2007;12:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous