Growth-inhibitory effects of a mineralized extract from the red marine algae, Lithothamnion calcareum, on Ca(2+)-sensitive and Ca(2+)-resistant human colon carcinoma cells
- PMID: 19394137
- PMCID: PMC2770718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.03.037
Growth-inhibitory effects of a mineralized extract from the red marine algae, Lithothamnion calcareum, on Ca(2+)-sensitive and Ca(2+)-resistant human colon carcinoma cells
Abstract
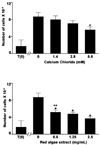
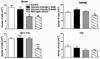
Proliferation and differentiation were assessed in a series of human colon carcinoma cell lines in response to a mineral-rich extract derived from the red marine algae, Lithothamnion calcareum. The extract contains 12% Ca2+, 1% Mg2+, and detectable amounts of 72 trace elements, but essentially no organic material. The red algae extract was as effective as inorganic Ca2+ alone in suppressing growth and inducing differentiation of colon carcinoma cells that are responsive to a physiological level of extracellular Ca2+ (1.4mM). However, with cells that are resistant to Ca2+ alone, the extract was still able to reduce proliferation and stimulate differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
All named authors of the original research paper entitled “Growth-inhibitory effects of a mineralized extract from the red marine algae,
Figures

References
-
- Kampman E, Slattery ML, Caan B, Potter JD. Calcium, vitamin D, sunshine exposure, dairy products and colon cancer risk (United States) Cancer Causes Control. 2000;11:459–466. - PubMed
-
- La Vecchia C, Braga C, Negri E, Franceschi S, Russo A, Conti E, Falcini F, Giacosa A, Montella M, Decarli A. Intake of selected micronutrients and risk of colorectal cancer. Int J. Cancer. 1997;73:525–530. - PubMed
-
- Baron JA, Beach M, Mandel JS, van Stolk RU, Haile RW, Sandler RS, Rothstein R, Summers RW, Snover DC, Beck GJ, Bond JH, Greenberg ER. Calcium supplements for the prevention of colorectal adenomas, Calcium Polyp Prevention Study Group. N. Engl J. Med. 1999;340:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Grau MV, Baron JA, Sandler RS, Haile RW, Beach ML, Church TR, Heber D. Vitamin D, calcium supplementation, and colorectal adenomas: results of a randomized trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1765–1771. - PubMed
-
- Holt PR, Wolper C, Moss SF, Yang K, Lipkin M. Comparison of calcium supplementation or low-fat dairy foods on epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation. Nutr. Cancer. 2001;41:150–155. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

