Serum complement activation on heterologous platelets is associated with arterial thrombosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid antibodies
- PMID: 19395455
- PMCID: PMC2707931
- DOI: 10.1177/0961203308099974
Serum complement activation on heterologous platelets is associated with arterial thrombosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid antibodies
Abstract
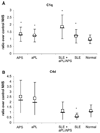
Complement plays a major role in inflammation and thrombosis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). A cross-sectional retrospective analysis was performed to evaluate serum complement fixation on platelets and thrombotic incidence using banked sera and clinical data from patients with SLE (n = 91), SLE with antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) or APS (n = 78) and primary aPL (n = 57) or APS (n = 96). In-situ complement fixation was measured as C1q and C4d deposition on heterologous platelets using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay approach. Platelet activation by patient serum in the fluid phase was assessed via serotonin release assay. Enhanced in-situ complement fixation was associated with the presence of IgG aPL and IgG anti-beta2 glycoprotein 1 antibodies (P < 0.05) and increased platelet activation (P < 0.005). Moreover, enhanced complement fixation, especially C4d deposition on heterologous platelets, was positively associated with arterial thrombotic events in patients with SLE and aPL (P = 0.039). Sera from patients with aPL possess an enhanced capacity for in-situ complement fixation on platelets. This capacity may influence arterial thrombosis risk in patients with SLE.
Figures

References
-
- Giannakopoulos B, Passam F, Rahgozar S, Krillis SA. Current concepts on the pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood. 2007;109:422–430. - PubMed
-
- Wilson WA, Gharavi AE, Koike T, et al. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;42:1309–1311. - PubMed
-
- Petri M. Epidemiology of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2000;15:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Machin SJ. Platelets and antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus. 1996;5:386–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

