Hemopexin down-regulates LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokines from macrophages
- PMID: 19395472
- PMCID: PMC2726768
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1208742
Hemopexin down-regulates LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokines from macrophages
Abstract
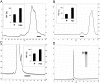
Detection of LPS in tissues is an integral component of innate immunity that acts to protect against invasion by Gram-negative bacteria. Plasma down-regulates LPS-induced cytokine production from macrophages, thereby limiting systemic inflammation in blood and distant tissues. To identify the protein(s) involved in this process, we used classical biochemical chromatographic techniques to identify fractions of mouse sera that suppress LPS-induced TNF from bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Fractionation yielded microgram quantities of a protein that was identified by MS to be hemopexin (Hx). Mouse Hx purified on hemin-agarose beads and rhHx decreased the production of cytokines from BMDMs and peritoneal macrophages induced by LPS. Preincubation of LPS with Hx did not affect the activity of LPS on LAL, whereas preincubation of Hx with macrophages followed by washing resulted in decreased activity of these cells in response to LPS, suggesting that Hx acts on macrophages rather than LPS. Heme-free Hx did not stimulate HO-1 in the macrophages. Purified Hx also decreased TNF and IL-6 from macrophages induced by the synthetic TLR2 agonist Pam3Cys. Our data suggest that Hx, which is an acute-phase protein that increases during inflammation, limits TLR4 and TLR2 agonist-induced macrophage cytokine production directly through a mechanism distinct from HO-1.
Figures

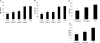

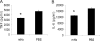
Comment in
-
Editorial: Hemopexin: newest member of the anti-inflammatory mediator club.J Leukoc Biol. 2009 Aug;86(2):203-4. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0309137. J Leukoc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19643739 No abstract available.
-
Hemopexin: anti-inflammatory, pro-inflammatory, or both?J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Jan;87(1):1-2; author reply 3, 5. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0809560. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20047881 No abstract available.
References
-
- Akashi S, Shimazu R, Ogata H, Nagai Y, Takeda K, Kimoto M, Miyake K. Cutting edge: cell surface expression and lipopolysaccharide signaling via the Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2 complex on mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 2000;164:3471–3475. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Akira S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 2005;17:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Bone R C, Balk R A, Cerra F B, Dellinger R P, Fein A M, Knaus W A, Schein R M H, Sibbald W J. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Angus D C, Linde-Zwirble W T, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky M R. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

