Inactivation of enteric viruses in minimally processed berries and herbs
- PMID: 19395576
- PMCID: PMC2698352
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00182-09
Inactivation of enteric viruses in minimally processed berries and herbs
Abstract
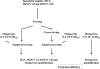
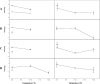
Several hepatitis A virus (HAV) and human norovirus (HuNoV) outbreaks due to consumption of contaminated berries and vegetables have recently been reported. Model experiments were performed to determine the effectiveness of freeze-drying, freeze-drying combined with heating, and steam blanching for inactivation of enteric viruses that might be present on the surface of berries and herbs. Inactivation of HAV and inactivation of feline calicivirus, a surrogate for HuNoV, were assessed by viral culturing and quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), whereas HuNoV survival was determined only by quantitative RT-PCR. While freeze-drying barely reduced (<1.3 log(10) units) the amount of HAV RNA detected in frozen produce, a greater decline in HAV infectivity was observed. The resistance of HuNoV genogroup I (GI) to freeze-drying was significantly higher than that of HuNoV GII on berries. Addition of a terminal dry heat treatment at 120 degrees C after freeze-drying enhanced virus inactivation by at least 2 log(10) units, except for HuNoV GII. The results suggest that steam blanching at 95 degrees C for 2.5 min effectively inactivated infectious enteric viruses if they were present in herbs. Our results provide data for adjusting food processing technologies if viral contamination of raw materials is suspected.
Figures

References
-
- Baert, L., M. Uyttendaele, M. Vermeersch, C. E. Van, and J. Debevere. 2008. Survival and transfer of murine norovirus 1, a surrogate for human noroviruses, during the production process of deep-frozen onions and spinach. J. Food Prot. 71:1590-1597. - PubMed
-
- Boxman, I. L., J. J. Tilburg, N. A. Te Loeke, H. Vennema, K. Jonker, E. de Boer, and M. Koopmans. 2006. Detection of noroviruses in shellfish in the Netherlands. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 108:391-396. - PubMed
-
- Butot, S., T. Putallaz, and G. Sanchez. 2008. Effects of sanitation, freezing and frozen storage on enteric viruses in berries and herbs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 126:30-35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

