The colorectal cancer risk at 18q21 is caused by a novel variant altering SMAD7 expression
- PMID: 19395656
- PMCID: PMC2694486
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.092668.109
The colorectal cancer risk at 18q21 is caused by a novel variant altering SMAD7 expression
Abstract
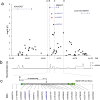
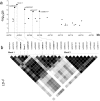
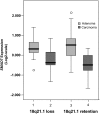
Recent genome-wide scans for colorectal cancer (CRC) have revealed the SMAD7 (mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7) gene as a locus associated with a modest, but highly significant increase in CRC risk. To identify the causal basis of the association between 18q21 variation and CRC, we resequenced the 17-kb region of linkage disequilibrium and evaluated all variants in 2532 CRC cases and 2607 controls. A novel C to G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) at 44,703,563 bp was maximally associated with CRC risk (P = 5.98 x 10(-7); > or =1.5-fold more likely to be causal than other variants). Using transgenic assays in Xenopus laevis as a functional model, we demonstrate that the G risk allele leads to reduced reporter gene expression in the colorectum (P = 5.4 x 10(-3)). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays provided evidence for the role of Novel 1 in transcription factor binding. We propose that the novel SNP we have identified is the functional change leading to CRC predisposition through differential SMAD7 expression and, hence, aberrant TGF-beta signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Broderick P., Carvajal-Carmona L., Pittman A.M., Webb E., Howarth K., Rowan A., Lubbe S., Spain S., Sullivan K., Fielding S., et al. A genome-wide association study shows that common alleles of SMAD7 influence colorectal cancer risk. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:1315–1317. - PubMed
-
- de Bruin E.C., van de Pas S., Lips E.H., van Eijk R., van der Zee M.M., Lombaerts M., van Wezel T., Marijnen C.A., van Krieken J.H., Medema J.P., et al. Macrodissection versus microdissection of rectal carcinoma: Minor influence of stroma cells to tumor cell gene expression profiles. BMC Genomics. 2005;6:142. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Gobbi M., Viprakasit V., Hughes J.R., Fisher C., Buckle V.J., Ayyub H., Gibbons R.J., Vernimmen D., Yoshinaga Y., de Jong P., et al. A regulatory SNP causes a human genetic disease by creating a new transcriptional promoter. Science. 2006;312:1215–1217. - PubMed
-
- Dermitzakis E.T., Reymond A., Antonarakis S.E. Conserved non-genic sequences - an unexpected feature of mammalian genomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:151–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
