Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation in prostate oncogenesis
- PMID: 19396167
- PMCID: PMC2898503
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.371
Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation in prostate oncogenesis
Abstract
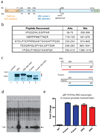
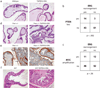
The TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, present in approximately 50% of prostate cancers, is less common in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN), raising questions about whether TMPRSS2-ERG contributes to disease initiation. We identified the translational start site of a common TMPRSS2-ERG fusion and showed that transgenic TMPRSS2-ERG mice develop PIN, but only in the context of PI3-kinase pathway activation. TMPRSS2-ERG-positive human tumors are also enriched for PTEN loss, suggesting cooperation in prostate tumorigenesis.
Figures
Comment in
-
TMPRSS2-ERG and PTEN loss in prostate cancer.Nat Genet. 2009 May;41(5):509-10. doi: 10.1038/ng0509-509. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19399032
Comment on
-
Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to promote cancer progression in the prostate.Nat Genet. 2009 May;41(5):619-24. doi: 10.1038/ng.370. Epub 2009 Apr 26. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19396168 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

