Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) expression and their prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 19397802
- PMCID: PMC2680906
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-125
Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) expression and their prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Similarly to other tumor types, an imbalance between unrestrained cell proliferation and impaired apoptosis appears to be a major unfavorable feature of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The members of IAP family are key regulators of apoptosis, cytokinesis and signal transduction. IAP survival action is antagonized by specific binding of Smac/DIABLO and XAF1. This study aimed to investigate the gene and protein expression pattern of IAP family members and their antagonists in a series of human HCCs and to assess their clinical significance.
Methods: Relative quantification of IAPs and their antagonist genes was assessed by quantitative Real Time RT-PCR (qPCR) in 80 patients who underwent surgical resection for HCC. The expression ratios of XIAP/XAF1 and of XIAP/Smac were also evaluated. Survivin, XIAP and XAF1 protein expression were investigated by immunohistochemistry. Correlations between mRNA levels, protein expression and clinicopathological features were assessed. Follow-up data were available for 69 HCC patients. The overall survival analysis was estimated according to the Kaplan-Meier method.
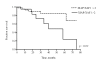
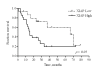
Results: Survivin and Livin/ML-IAP mRNAs were significantly over-expressed in cancer tissues compared to non-neoplastic counterparts. Although Survivin immunoreactivity did not correlate with qPCR data, a significant relation was found between higher Survivin mRNA level and tumor stage, tumor grade and vascular invasion.The mRNA ratio XIAP/XAF1 was significantly higher in HCCs than in cirrhotic tissues. Moreover, high XIAP/XAF1 ratio was an indicator of poor prognosis when overall survival was estimated and elevated XIAP immunoreactivity was significantly associated with shorter survival.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that alterations in the expression of IAP family members, including Survivin and Livin/ML-IAP, are frequent in HCCs. Of interest, we could determine that an imbalance in XIAP/XAF1 mRNA expression levels correlated to overall patient survival, and that high XIAP immunoreactivity was a poor prognostic factor.
Figures

References
-
- Poma P, Notarbartolo M, Labbozzetta M, Sanguedolce R, Alaimo A, Carina V, Maurici A, Cusimano A, Cervello M, D'alessandro N. Antitumor effects of the novel NF-κB inhibitor dehydroxymethyl-epoxyquinomicin on human hepatic cancer cells: Analysis of synergy with cisplatin and of possible correlation with inhibition of pro-survival genes and IL-6 production. Int J Oncol. 2006;28(4):923–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

